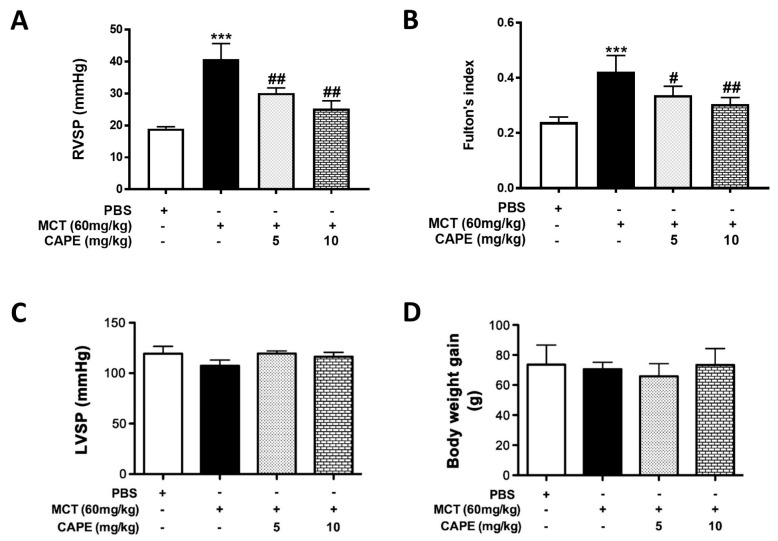
Figure 1.
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) improves monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in rats. (A) Rats were treated with CAPE (n = 6, 5 or 10 mg/kg) from day 14 to 28 after MCT injection (60 mg/kg). The rats in the healthy group received PBS injection instead of MCT (n = 5). Assessment of right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP), (B) right ventricular hypertrophy (Fulton index, the ratio of right ventricular weight to left ventricular plus septal weight, (C) left ventricular systolic pressure (LVSP), and (D) body weight in rats. Data in A and B are expressed as mean ± SEM of five independent experiments. *** p < 0.01, as compared with the PBS group. # p < 0.05; ## p < 0.01, as compared with the rats exposed to MCT alone.