FIGURE 9.
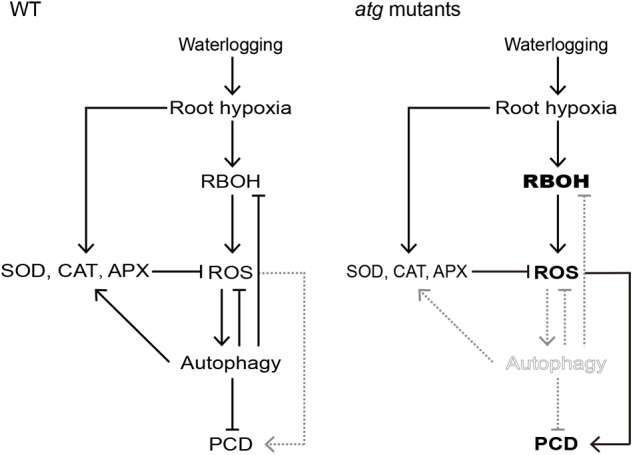
Proposed working model for signaling pathways that regulate PCD in Arabidopsis roots. In waterlogged wild-type roots, hypoxia induces both RBOH expression (leading to an increase in ROS), as well as increasing the expression and activities of ROS-scavenging enzymes CAT, APX, and SOD. The RBOH-dependent increase in ROS activates autophagy which alleviates PCD. However, autophagy deficiency of the atg mutants disrupts the induction of antioxidant enzymes expression and the inhibition of RBOH expression by autophagy. In that case, excessive accumulation of ROS contributes to PCD in atg mutant roots.
