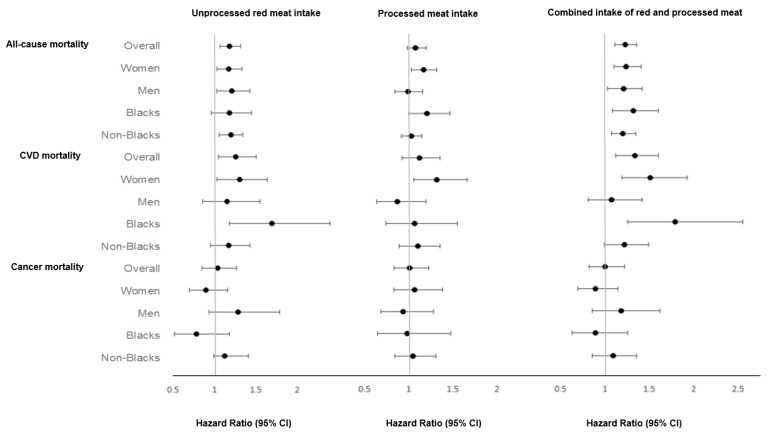
Figure 1.
Subgroup analysis by sex and race of the association between red meat and processed meat intake and all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality. Multivariable hazard ratios for mortality comparing the 90th percentiles (sex- and race-specific values) of unprocessed red and processed meats intakes and both combined with zero-intake (90th vs. 0) were adjusted for age; sex (not in sex subgroup analysis); race (not in race subgroup analysis); marital status; education level; multivitamin use; smoking; alcohol use; exercise; sleeping hours; body mass index (BMI); diabetes mellitus; hypertension; hypercholesterolemia; aspirin use; the use of blood pressure medications for at least 2 years in the last 5 years; the use of statin for at least 2 years in the last 5 years; menopausal status in women and hormone replacement therapy (HRT) among postmenopausal women; dietary energy; and dietary variables including cruciferous vegetables, fruits, whole grain, legumes, nuts and seeds, total dairy, eggs, fish, and unprocessed poultry.