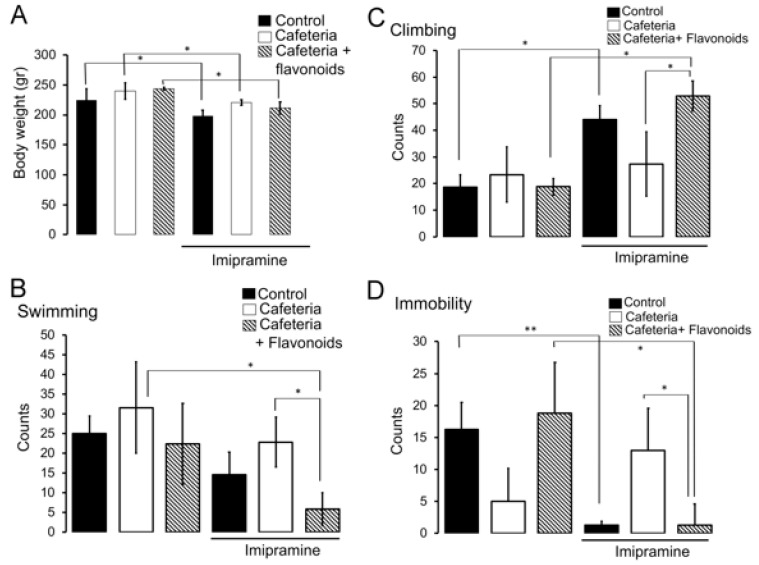
Figure 4.
Flavonoids revert depressive-like behavior induced by cafeteria diet exposure. (A) Offspring body weight after intraperitoneal imipramine (30 mg/kg) administration 40 min previous to test session. Nutritional programming induced by cafeteria (n = 8), cafeteria + flavonoids (n = 8), or standard chow diet (n = 7) was performed and i.p. imipramine administration to the cafeteria (n = 8), cafeteria + flavonoids (n = 8), or standard chow diet (n = 7), followed by the forced swim test, was accomplished as described previously. Total swimming (B), climbing (C) or immobility (D) counts/5 min were quantified as shown in graphs as mean ± SD. Statistical significance used Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by a Dunn’s Multiple Comparison Test, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.