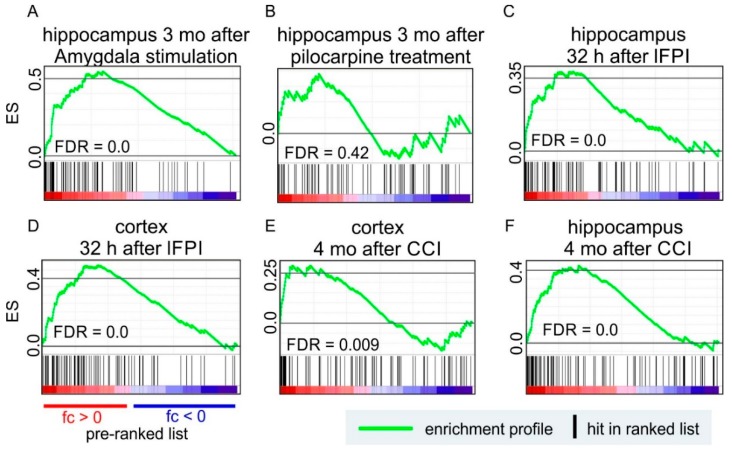
Figure 2.
The effect of epileptogenesis and epilepsy on EV-related genes in four rodent models of epileptogenesis: (i) status epilepticus (SE) triggered by electrical stimulation of the amygdala [92]; (ii) SE induced by intraperitoneal injection of a chemoconvulsant, pilocarpine [92]; (iii) traumatic brain injury (TBI) induced by lateral fluid-percussion [90]; and (iv) TBI induced with controlled cortical injury (CCI) in mice [91]. Gene expression data of the hippocampus or cortex was used to construct the rank list in Gene Set Enrichment Analysis. Top100 EV-related proteins from Vesiclepedia (http://microvesicles.org/, accessed on: 1 December 2018) were used to construct a gene set. The EV related genes were (A) positively enriched at 3 months (mo) in the amygdala stimulation SE-model, whereas (B) no enrichment was observed at 3 months in the pilocarpine SE-model. In the two TBI models of epileptogenesis, EV-related genes were positively enriched in the hippocampus and cortex at both (C,D) the acute (32 h post- TBI) and (E,F) chronic (4 months post-TBI) time point. Abbreviations: ES, enrichment score; FDR, false discovery rate; fc, fold change.