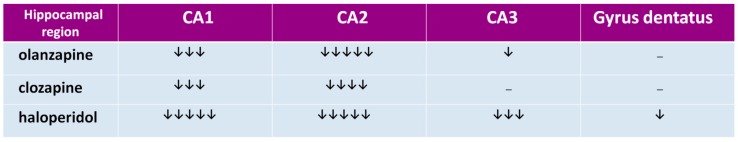
Figure 3.
The influence of chronic antipsychotic drug administration on glutamatergic activity in CA1, CA2, and CA3 hippocampus regions and in gyrus dentatus in rats. A number of arrows indicate the neuroleptic’s potential to decrease the glutamatergic activity, resulting from the summation of NR1 expression, and proportion of NR2A to NR2B expression (an arrow was added when NR2B expression prevailed, and subtracted when NR2A expression prevailed).