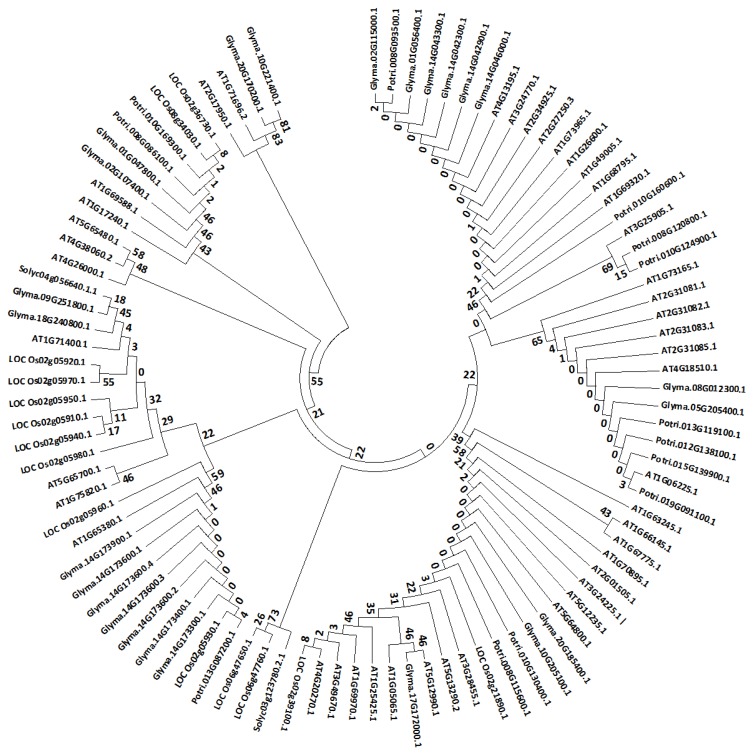
Figure 3.
Molecular phylogenetic analysis of stem cell-related proteins. Analysis was performed using the stem cell-related protein sequences from Arabidopsis, rice, soybean, tomato, and poplar. The evolutionary history was inferred by using the maximum likelihood method based on the JTT (Jones Taylor-Thornton) matrix-based model [1]. The tree with the highest log likelihood (–34197.0000) is shown. The initial tree(s) for the heuristic search were obtained automatically by applying the neighbor-join (NJ) and BioNJ algorithms to a matrix of pairwise distances estimated using the JTT model, and then selecting the topology with a superior log likelihood value. The analysis involved 97 amino acid sequences. All of the positions with less than 95% site coverage were eliminated; that is, fewer than 5% alignment gaps, missing data, and ambiguous bases were allowed at any position, leaving only three positions in the final dataset. The evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA7 [2].