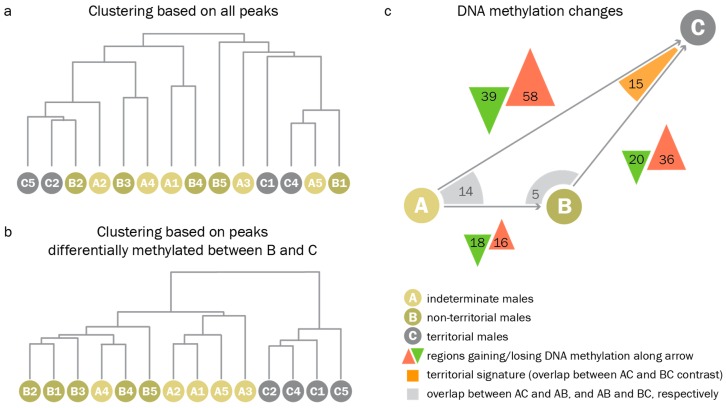
Figure 5.
Indeterminate males do not display territorial DNA methylation patterns. (a). Clustering based on genome wide principal component analysis (PCA) eigenvalues based on read counts of all peak regions. Indeterminate, non-territorial, and territorial males are distributed randomly throughout the tree. (b). Clustering based on regions differentially methylated between non-territorial and territorial males. Branches for indeterminate, non-territorial, and territorial males cluster within the respective groups. Additionally, indeterminate males cluster with non-territorial males. (c). Results of pairwise comparisons. Green and red triangles represent regions that gain/lose DNA methylation during the transition represented by the grey arrow. Arrow lengths and triangle areas are drawn to scale to represent the number of regions with differential DNA methylation. Differentially methylated regions that overlap between two comparisons are indicated by orange/grey corners.