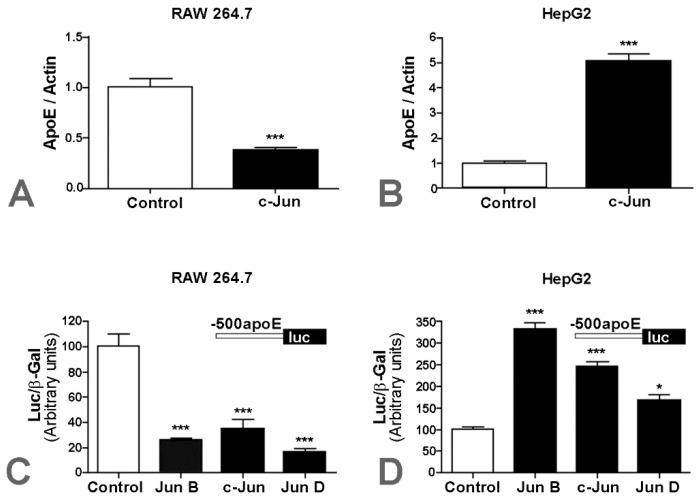
Figure 1.
Cell-specific effects of c-Jun on apolipoprotein E (apoE) gene expression in macrophages and hepatocytes. RAW 264.7 (A) and HepG2 (B) cells were transfected with c-Jun-encoding plasmids, and apoE gene expression was determined by real-time PCR. Overexpression of c-Jun in RAW 264.7 cells caused a reduction in apoE mRNA level down to ~40% of the basal apoE level (p < 0.01). By contrast, c-Jun overexpression in HepG2 cells induced a ~5-fold increase in apoE mRNA levels (p < 0.001), compared to control cells; RAW 264.7 (C) and HepG2 (D) cells were transiently transfected with the construct −500apoE in the absence (control) or in the presence of JunB, c-Jun, or JunD expression vectors. In RAW 264.7, cell JunB overexpression reduced apoE promoter activity to ~25% of the control value, c-Jun caused a reduction of activity to ~30% of the control, and JunD reduced its activity to ~20% of the control (p < 0.001 for each case). By contrast, the overexpression of JunB in HepG2 cells increased apoE promoter activity (p < 0.001) ~3.4-fold, c-Jun increased its activity (p < 0.01) ~2.6-fold, and JunD increased apoE promoter activity (p < 0.05) 1.6-fold.