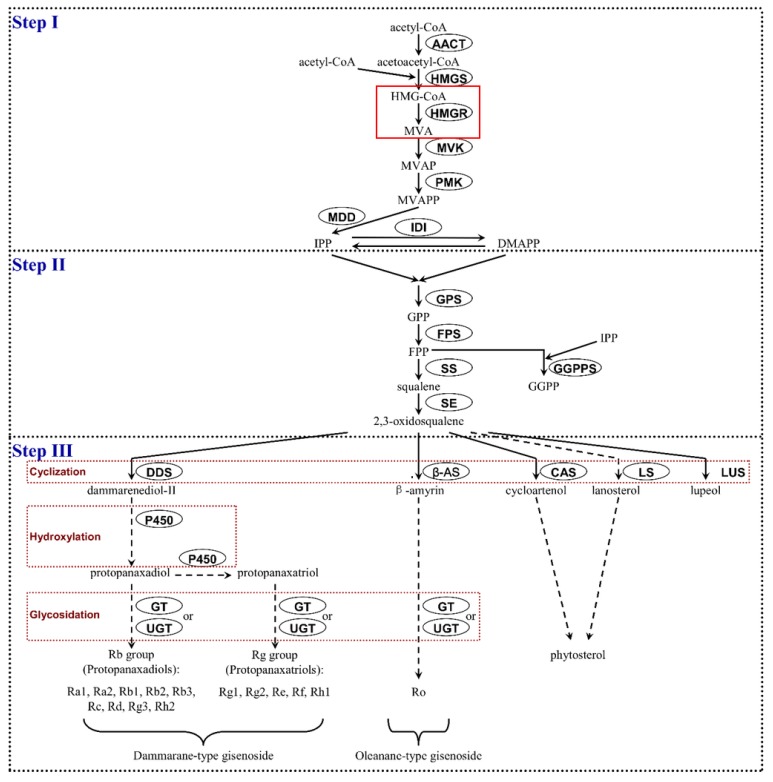
Figure 1.
Biosynthetic pathway of ginsenosides according to [6]. AACT—acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase; HMGS—HMG-CoA synthase; HMGR—HMG-CoA reductase; MVA—mevalonate; MVK—mevalonate kinase; MVAP—mevalonate phosphate; PMK—phosphomevalonate kinase; MVAPP—mevalonate diphosphate; MDD—mevalonate-5-diphosphate decarboxylase; IDI—isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase; IPP—isopentenyl diphosphate, DMAPP—dimethylallyl diphosphate, GPS—geranyl diphosphate synthase; GPP geranyl diphosphate, FPS—farnesyl diphosphate synthase; FPP—farnesyl diphosphate, SS—squalene synthase; SE—squalene epoxidase, GGPPS—geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase; GGPP—geranylgeranyl diphosphate; DDS—dammarenediol synthase; P450—cytochrome P450; GT—glycosyltransferase; UGT—UDP-glycosyltransferase, β-AS—beta-amyrin synthase; CAS—cycloartenol synthase; LS—lanosterol synthase; LUS—lupeol synthase. Solid red-frame means the reaction catalyzed by HMGR enzyme; Dotted red-frame—putative late steps of ginsenoside biosynthesis; dotted arrow—putative reaction steps leading to individual ginsenosides and phytosterol, solid arrows—well recognized reaction steps in ginsenoside biosynthesis pathway.