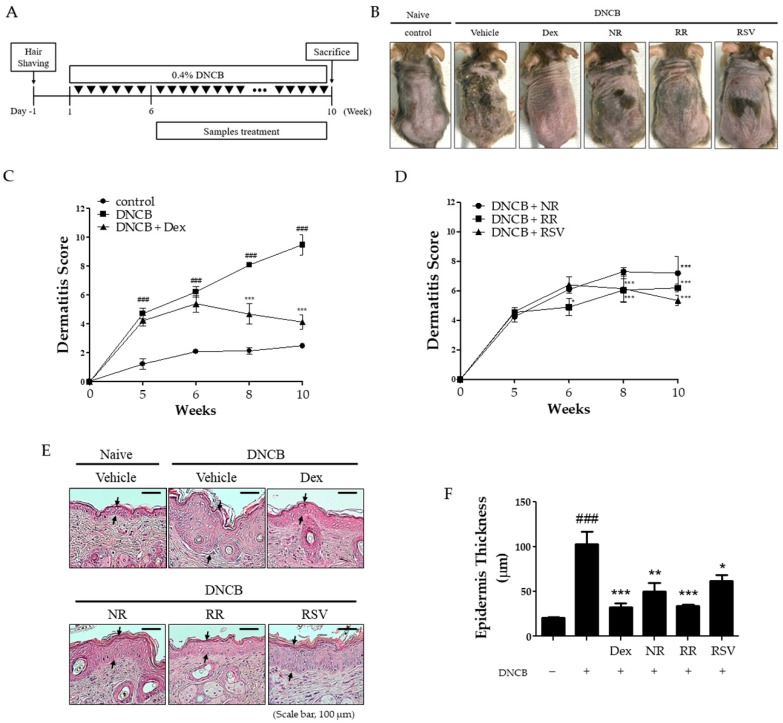
Figure 1.
Effect of RR on the development of atopic dermatitis (AD) in DNCB-induced NC/Nga mice. (A) Schematic presentation of the animal experiment schedule. Mice were divided into five groups (n = 7 per group). After the induction of AD-like symptoms with DNCB, NR, RR, and RSV were topically applied thrice weekly for five weeks. (B) Images of dorsal skin were taken on the last day of the experiment. (C,D) The dermatitis score was defined as the sum of score for five clinical indexes: erythema, edema, erosion, dryness, and lichenification. (E) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of dorsal skin. Scale bar = 100 μm. Arrows indicate the thickness of epidermis. (F) Histogram of hematoxylin and eosin staining. Values are expressed as means ± SEM. ### p < 0.001 versus vehicle group; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 versus DNCB-treated group. Dex, dexamethasone; NR, normal rice; RR, resveratrol-enriched rice; RSV, resveratrol.