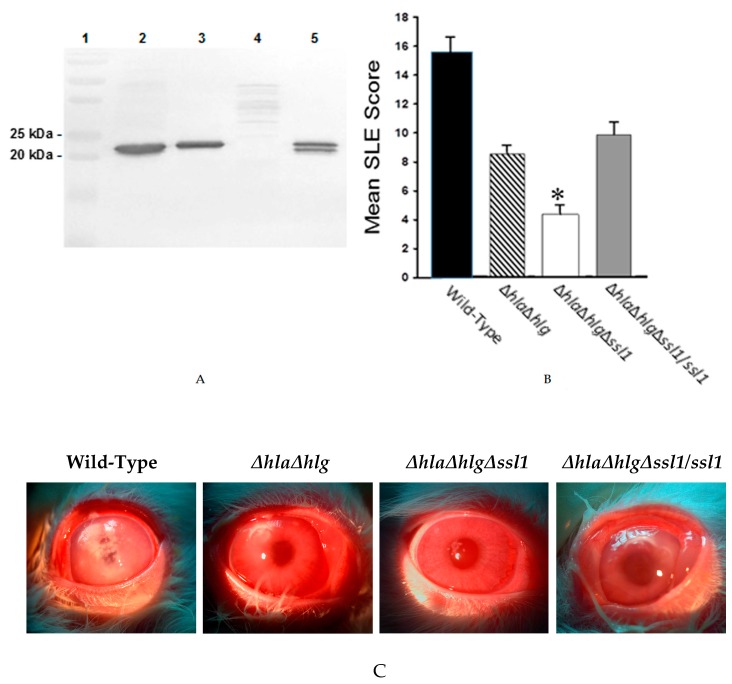
Figure 7.
Phenotype confirmation and virulence of S. aureus strain Newman and the isogenic mutants. (A) Western blot analysis of concentrated culture supernatants of wild-type strain Newman and the mutants. Lane 1: molecular weight standards; Lane 2: strain Newman; Lane 3: double mutant (Newman ΔhlaΔhlg); Lane 4: triple mutant (Newman ΔhlaΔhlgΔssl1), and Lane 5: rescue strain (Newman ΔhlaΔhlgΔssl1/ssl1). The blot was developed using rabbit polyclonal antibody to recombinant SSL1. (B) Slit lamp examination scoring (SLE) of rabbit eyes 24 h after infection with strain Newman ( ), the double mutant (
), the double mutant ( ), the triple mutant (
), the triple mutant ( ), or the rescue strain (
), or the rescue strain ( ). The SLE score for eyes infected with the triple mutant was significantly lower than that of eyes infected with the wild-type Newman, the double mutant, or the rescue strain (*, P ≤ 0.001). (C) Photographs of rabbit eyes 24 h after intrastromal injection with 100 CFU of strain Newman, the double mutant (Newman ΔhlaΔhlg), the triple mutant (Newman ΔhlaΔhlgΔssl1), or the rescue strain (Newman ΔhlaΔhlgΔssl1/ssl1). These eyes contained similar log CFU per cornea (P = 0.19).
). The SLE score for eyes infected with the triple mutant was significantly lower than that of eyes infected with the wild-type Newman, the double mutant, or the rescue strain (*, P ≤ 0.001). (C) Photographs of rabbit eyes 24 h after intrastromal injection with 100 CFU of strain Newman, the double mutant (Newman ΔhlaΔhlg), the triple mutant (Newman ΔhlaΔhlgΔssl1), or the rescue strain (Newman ΔhlaΔhlgΔssl1/ssl1). These eyes contained similar log CFU per cornea (P = 0.19).