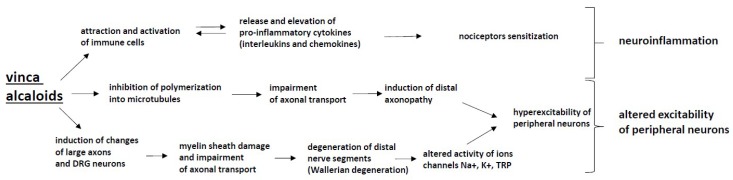
Figure 5.
The mechanisms of CIPN induced by vinca alkaloids: Vinca alkaloids cause changes to large axons and DRG neurons, which leads to Wallerian degeneration, the altered activity of ion channels and the hyperexcitability of peripheral neurons. Moreover, the inhibition of polymerization into microtubules inhibits axonal transport, which leads to distal axonopathy. These processes alter the excitability of peripheral neurons, whereas the attraction and activation of immune cells by vinca alkaloids causes the release and elevation of pro-inflammatory cytokines (interleukins and chemokines), which results in neuroinflammation.