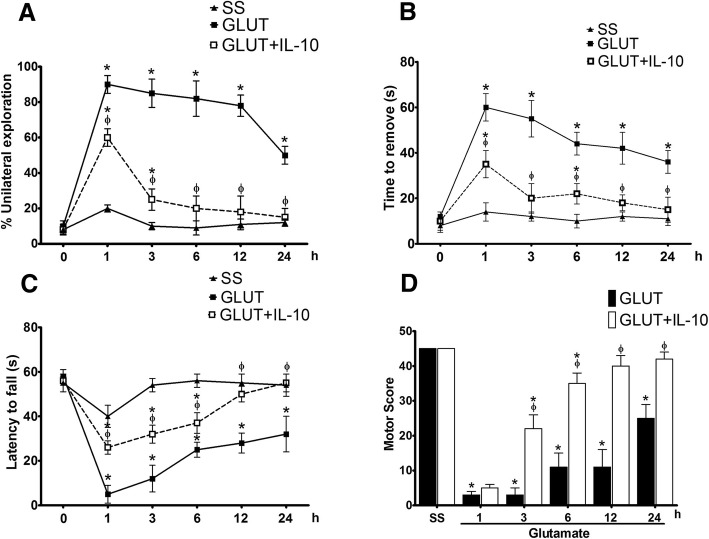
Fig. 13.
IL-10 improves motor recovery in wild-type mice after glutamate administration. Motor behavior of wild-type mice injected with NaCl 0.9% (SS), 1 M glutamate (GLUT) and glutamate + 0.4 ng/mL of IL-10 (GLUT + IL-10), was evaluated in three tests of motor behavior at 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h after glutamate intracerebral injection. a Cylinder test, in which each mouse obtained a percentage based on the ratio of unilateral and bilateral explorations performed in three trials, of 3 min each; the percentage was expressed as mean ± SEM of six independent tests. b Adhesive removal test quantifies the time in which the animals remove a label previously placed by the examiner. The time of removal was quantified in seconds and was expressed as means ± SEM of six independent tests. c Inverted grid test was evaluated by exposing the mice to the inverted grid test in which the decay time was quantified for three non-consecutive opportunities of a maximum of 60 s of duration. The results are expressed as means ± SEM of the latency to fall of six independent tests. d Integration of behavioral performance of three previous tests was carried out by assigned an arbitrary score to the performance of each animal, giving the highest score to the performance of the mice injected with saline (45 points). The results are expressed in arbitrary units of motor score as the mean ± SEM of the latency to fall of six independent tests. *p < 0.05 vs the corresponding saline control; ϕp < 0.05 vs corresponding mouse treated with glutamate alone