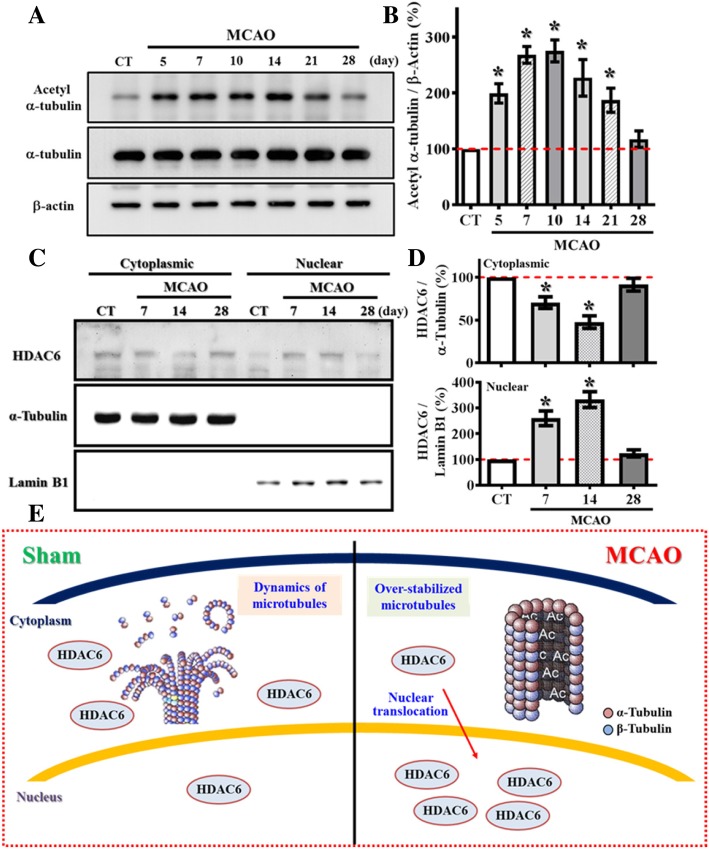
Fig. 6.
Aberrant nuclear translocation of HDAC6 after stroke causes hyper-acetylation of α-tubulin. (a) Representative western blot images of the acetylated-α-tubulin at Lys40, α-tubulin and β-actin levels at different time points after MCAO surgery. (b) Quantification of the acetylated-α-tubulin that normalized to β-actin after MCAO surgery. n = 4 biological replicates, * p < 0.05 compared to sham operated control. (c) Representative western blot images of the HDAC6 distributed between cytosolic or nuclear fractions at different time points after MCAO surgery. α-tubulin and Lamin B1 act as the internal control for either cytosolic or nuclear fraction. (d) Quantification of the cytoplasmic (top) or nuclear (bottom) protein levels of HDAC6 that normalized to its internal controls at different time points after MCAO. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. n = 5, * p < 0.05 compared to sham operated control. (e) A cartoon model illustrates the aberrant nuclear translocation of HDAC6 after stroke that causes hyper-acetylation α-tubulin