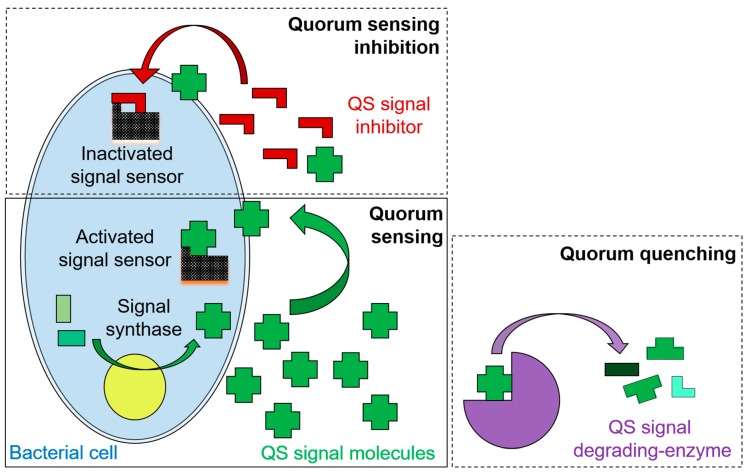
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of a quorum sensing (QS) system and its interruption mechanisms: quorum quenching (QQ) and QS inhibition (QSI). The QS signals (green crosses) are synthesized by a synthase from the metabolic pool of the bacterial cell. They diffuse out of the cell and their presence is sensed by a bacterial sensor protein once a threshold cell, hence signal concentration, is reached (lower left panel). QS signals can however be degraded by enzymatic activity (lower right panel), preventing their detection by the bacterial cells. The presence of QS inhibitors (red L-shape figures, upper left panel) inactivate the sensors, hindering the detection of the QS signals. Both mechanisms (QQ and QSI) lead to a reduced or abolished expression of QS regulated genes.