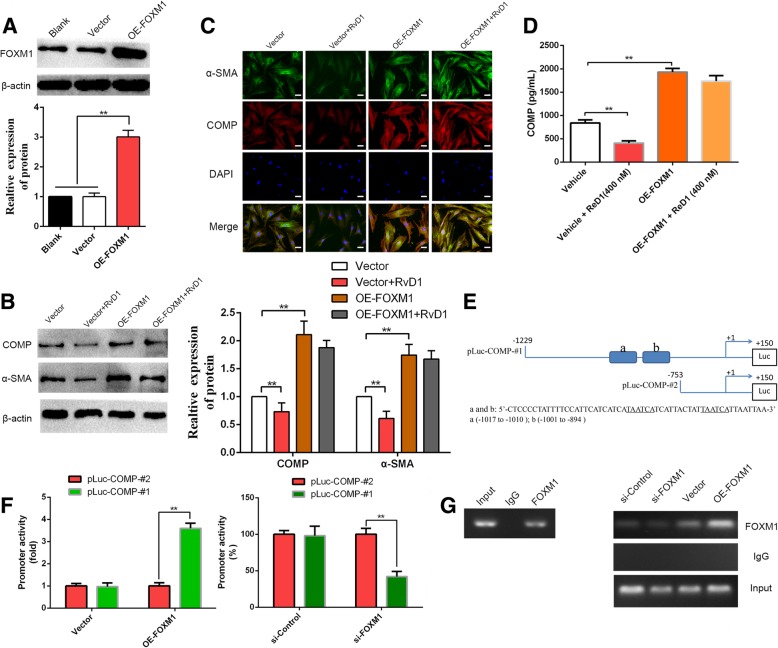
Fig. 7.
RvD1-mediated inhibits COMP expression through abrogation of FOXM1 recruitment to its promoter. (a) pcDNA/FOXM1 could significantly increase FOXM1 expression in CAFs at protein level. n = three independent experiments, ** P < 0.01 by ANOVA. (b-c) pcDNA/ Control and pcDNA/ FOXM1 were transfected into CAFs then treated with RvD1, the expression of α-SMA and COMP were examined by western blotting and double immunofluorescence analysis. Magnification is × 400, and scale bars = 20 μm. n = three independent experiments, ** P < 0.01 by ANOVA. (d) pcDNA/ Control and pcDNA/ FOXM1 were transfected into CAFs then treated with RvD1, the serection of COMP was measured by Elisa assay. n = three independent experiments, ** P < 0.01 by ANOVA. (e) The sequences and positions of putative FOXM1-binding elements on the COMP promoter. (f) CAFs were co-transfected with the COMP promoter–luciferase construct pLuc–COMP#1 or pLuc–COMP#2, and 50 nmol/L siFOXM1 or control siRNA, and pcDNA3.1-FOXM1 or pcDNA3.1-vector. Promoter activity was measured by a dual luciferase assay kit. n = three independent experiments, ** P < 0.01 by ANOVA. (g) Chromatins were extracted from CAFs, CAFs-siControl, CAFs-siFOXM1, CAFs-vector and CAFs-OE-FOXM1, and the binding of FOXM1 to the COMP promoter was detected by the ChIP assay