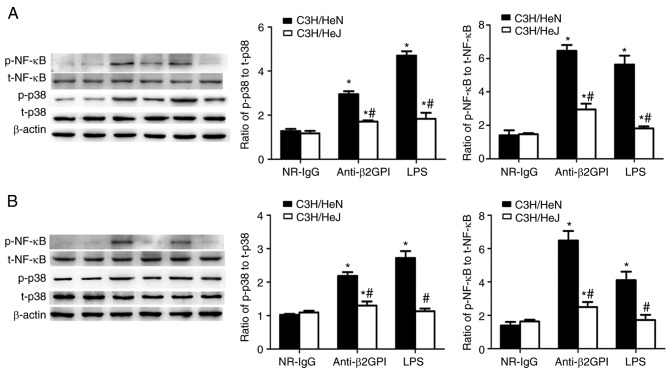
Figure 5.
Involvement of TLR-4 in anti-β2GPI–IgG-stimulated phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and NF-κB p65 during the expression of inflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules. C3H/HeN mice (n=8 in each group) and C3H/HeJ mice (n=8 in each group) were treated by intraperitoneal injection of anti-β2GPI–IgG (100 µg antibody per injection) at time 0 and 48 h. The peritoneal macrophages and aortas were collected at 72 h after the first injection. The positive control group was challenged with LPS (1 µg/g body weigh) 2 h before the experiments. Protein samples were isolated from (A) peritoneal macrophages and (B) homogenate of aortas using a proteome extraction kit. The phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and the p65 subunit of NF-κB were measured by western blotting with their corresponding antibodies. The western blot and the quantitative data are representative of three separated experiments with the similar result. *P<0.05 vs. control NR-IgG; #P<0.05 vs. corresponding C3H/HeN stimulation group. TLR-4, Toll-like receptor-4; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; p-, phospho; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; t-, total; NR-IgG, isotype control antibody; Anti-β2GPI, anti-β2-glycoprotein I; LPS, lipopolysaccharide.