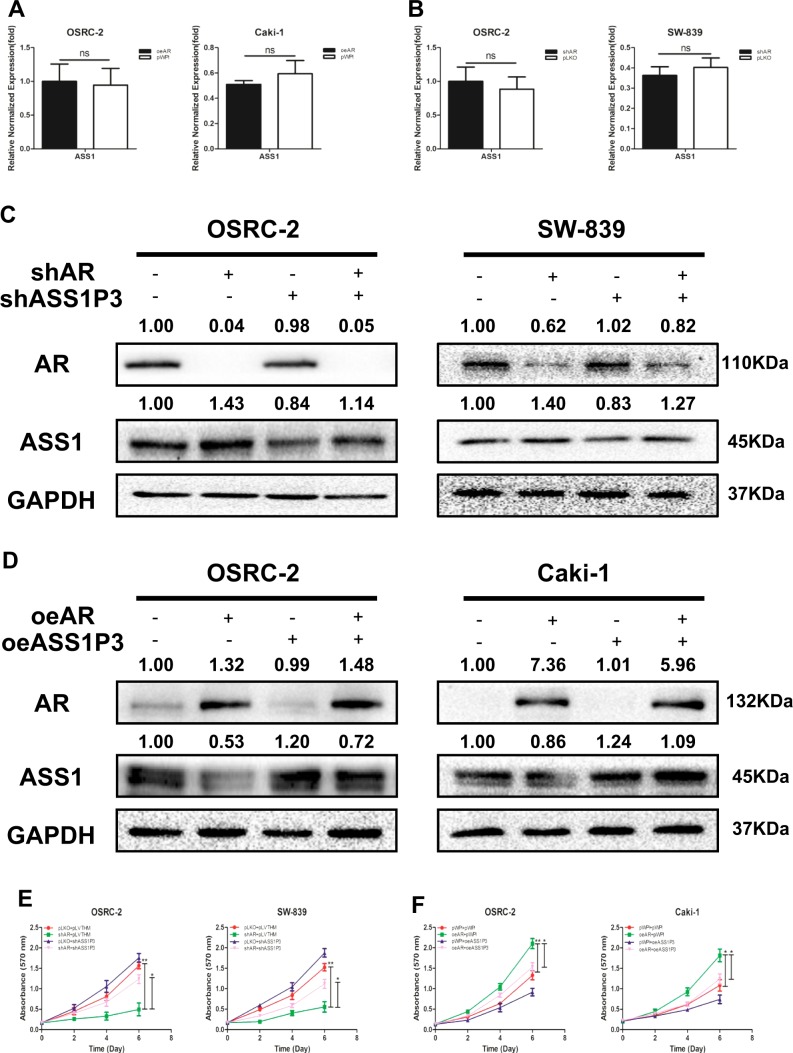
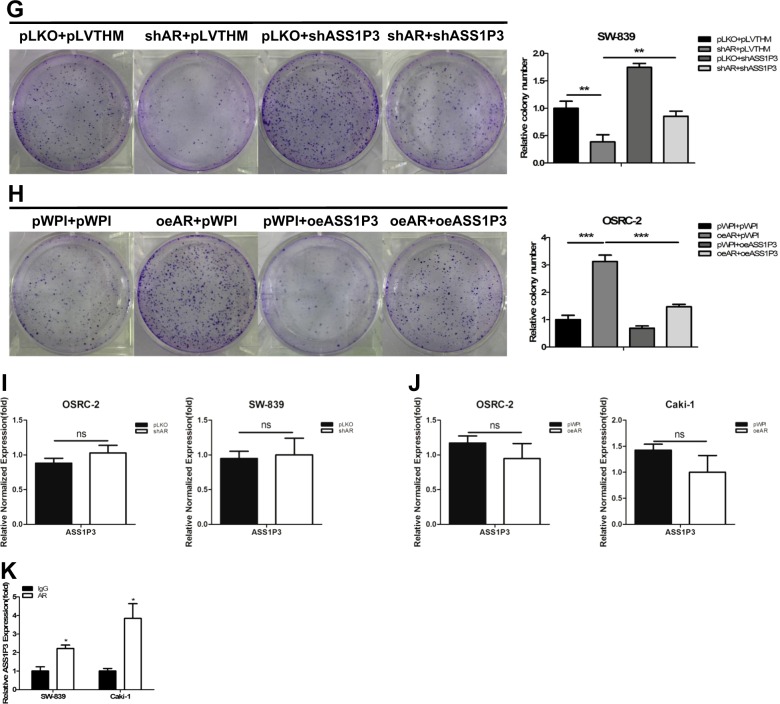
Fig. 3. AR could suppress ASS1 to promote RCC proliferation through ASS1P3.
a Real-time RT-PCR assay was applied to detect the expression of ASS1 in OSRC-2 and Caki-1 cells with overexpressed AR compared with pWPI. b Real-time RT-PCR assay was applied to detect the expression of ASS1 in OSRC-2 and SW-839 cells with knocked-down AR compared with pLKO. c Western blot assay shows that ASS1P3-shRNA could partially reverse the AR-shRNA-increased ASS1 expression in OSRC-2 and SW-839 cells. d Western blot assay shows that ASS1P3 could partially reverse the AR-decreased ASS1 expression in OSRC-2 and Caki-1 cells. e MTT assay shows that ASS1P3-shRNA could partially reverse the AR-shRNA-increased ASS1 expression in OSRC-2 and SW-839 cells. f MTT assay shows that ASS1P3 could partially reverse the AR-decreased ASS1 expression in OSRC-2 and Caki-1 cells. g Colony formation assay shows that ASS1P3-shRNA could partially reverse the AR-shRNA-increased ASS1 expression in SW-839 cells. h Colony formation assay shows that ASS1P3 could partially reverse the AR-decreased ASS1 expression in OSRC-2 cells. i Real-time RT-PCR assay was applied to detect the expression of ASS1P3 by knocking down AR compared with pLKO in OSRC-2 and SW-839 cells. j Real-time RT-PCR assay was applied to detect the expression of ASS1P3 in overexpressed AR compared with pWPI in OSRC-2 and Caki-1 cells. k RIP assay was performed to detect the interaction between AR and ASS1P3 after adding AR and IgG to SW-839 and Caki-1 cells, respectively. For A-B, E-F, G-K, data are presented as mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ns = not significant, compared to the controls