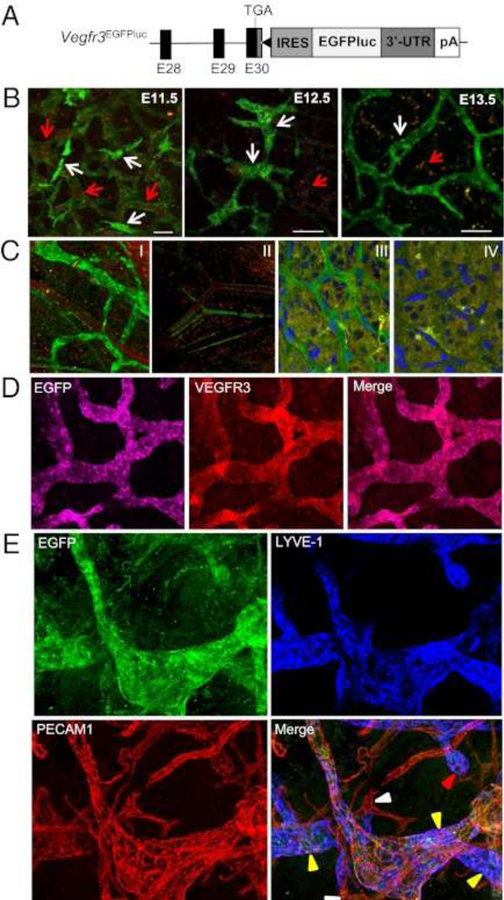
Figure 13. Vegfr3 expression shifts during early development from VECs to LECs.
(A) Schematic structure of the 3′ region of the Vegfr3EGFPLuc KI allele. The last three coding exons of the Vegfr3 gene (E28 to E30) are represented by black boxes. The 3′-UTR (dark gray box), the position of the stop codon (TGA), and the Vegfr3 polyadenilation signal (pA) are also shown. The black triangle represents an frt site remaining after Flp-mediated excision of the neomycin resistance cassette used for gene targeting. (B) Whole-body confocal images (EGFP) of Vegfr3-expressing cells during lymphatic vessel development in E11.5-E13.5 Vegfr3EGFPLuc (KI/KI) embryos. EGFP expression is seen in blood vessels (identified by the autofluorescence of the erythrocytes [red arrows]) at E11.5, while at E13.5 EGFP expression becomes restricted to the lymphatic vessels. Scale bar, 50 μm. (C) Confocal overlay of red and green channels of the ear skin (I and II) and retina (III and IV) from 3-week- and 7-day-old animals, respectively. Vegfr3EGFPLuc (KI/KI) mice (I and III). Wild-type mice (II and IV). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (II and IV). (D) Confocal images of EGFP and VEGFR3 whole-mount immunofluorescence staining of the ear skin from 2-week-old mice. (E) Expression of EGFP, LYVE-1 and PECAM1 in lymphatic vessels in the skin. Initial lymphatic capillaries (yellow arrowheads), some with blunt endings (red arrowhead), are EGFP+ and LYVE-1+. In PECAM1+ blood vessels (white arrowheads), only autofluorescence of red blood cells was detected. Reprinted with permission from [48].