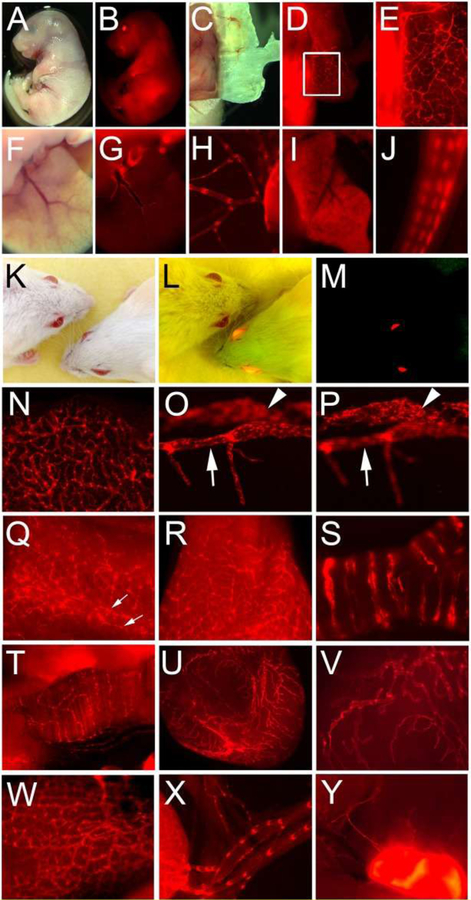
Figure 7. Prox1-tdTomato expression in reporter mouse embryos and adults.
(A-J) Embryonic tissues: bright field (A) and fluorescence (B) images of the Prox1-tdTomato embryo (E17.5). Distinct lymphatic networks shown in the embryonic skin (C-E). Panel E shows an enlarged image of the boxed area in panel D. Lymphatic vessels in the embryonic liver (F,G) and mesentery membrane (H). Note that hepatocytes (I) and tail nerves (J) were also positive for tdTomato. (K-Y) Adult tissues: headshots of adult wild-type and Prox1-tdTomato transgenic mice taken under a bright light (K), bright and fluorescent light (L) and fluorescent light (M). Lymphatic vessels were easily detectable in the ear (N), eye (O,P), tail (Q), tongue (R), trachea (S), diaphragm muscle (T), bladder (U,V), intestine (W), mesentery (X) and lymph node (Y). Corneal limbal lymphatic (arrow) and Schlemm’s canal (arrowhead) of the eye are shown in two consecutive focal planes (O,P). Bilateral lymphatic collectors in the tail were marked with two arrows (Q). Reprinted with permission from [45].