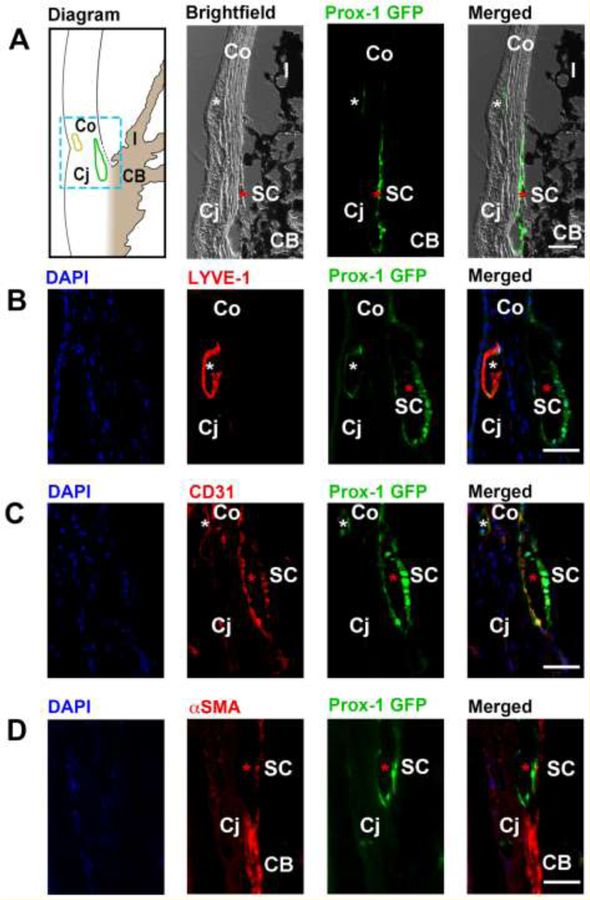
Figure 9. Cross-sectional immunohistochemical analysis of the iridocorneal angle of adult Prox-1-GFP mice.
(A) Left panel, diagram of anterior chamber angle showing location of Schlemm’s canal (green) at the corneoscleral junction. Yellow, limbal lymphatic vessels. Middle to right panels: brightfield, green fluorescent, and merged micrographs corresponding to the boxed region of interest in the diagram. White asterisks: limbal lymphatics; red asterisks: Schlemm’s canal. (B) Representative images showing the LYVE-1+Prox-1+ limbal lymphatic vessel (white asterisk) located between the cornea and conjunctiva, and the LYVE- 1−Prox1+ Schlemm’s canal (red asterisk) located nearby. Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining; red: LYVE-1; green: Prox-1. (C) Representative images showing that both limbal lymphatics (white asterisk) and the Schlemm’s canal (red asterisk) expressed CD31, a panendothelial cell marker. Blue: DAPI; red: CD31; green: Prox-1. (D) Representative images showing absence of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expression on the Prox-1+ Schlemm’s canal (red asterisk), but expression of α-SMA on adjacent positive control tissue of the ciliary body. Blue: DAPI; red: αSMA; green: Prox-1. Scale bars, 50 µm (A–D). SC, Schlemm’s canal; Co, cornea; Cj, conjunctiva; I, iris; CB: ciliary body. Reprinted with permission from [56].