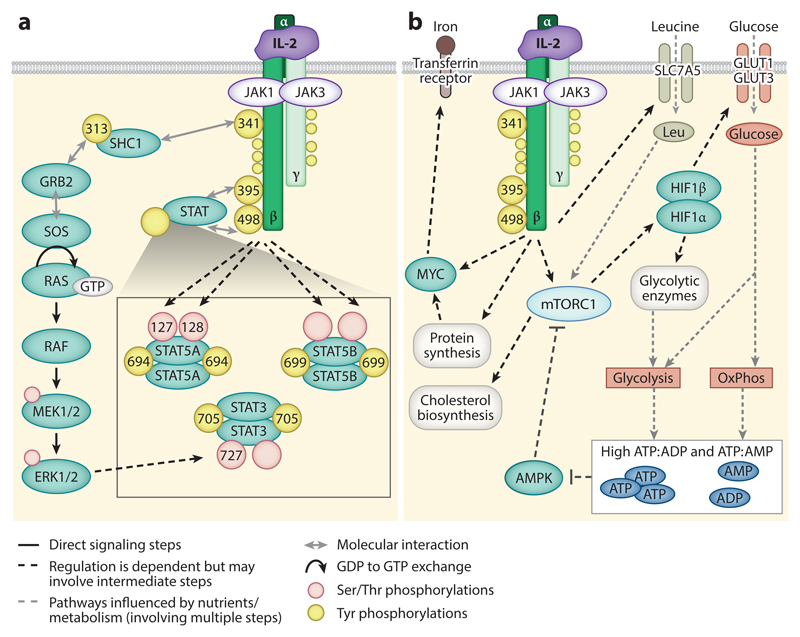
Figure 2.
Signaling downstream of the IL-2 receptor (IL-2R): (a) Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) signal transduction. The IL-2Rβ chain couples to JAK1, and the γ chain (γc) couples to JAK3. IL-2R occupancy results in the activation of the JAKs and the tyrosine phosphorylation of IL-2Rβ and γc (yellow circles). The tyrosine phosphorylations in IL-2Rβ are best characterized in terms of the signaling complexes they coordinate; the phosphorylation of Y395 and Y498 (in murine IL-2Rβ) permits the recruitment of STAT5A, STAT5B, and STAT3, while the phosphorylation of Y341 allows recruitment of SHC1. Following their recruitment to the receptor, STAT5 proteins and SHC1 are tyrosine phosphorylated by JAKs. Tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT5 permits dimerization, nuclear translation, and STAT5-mediated transcription. Tyrosine phosphorylation of SHC1 allows the recruitment of GRB2 and SOS to facilitate GTP loading of Ras and activation of the classical Raf-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase) cascade. STAT proteins are also phosphorylated on serine residues (peach circles) in response to IL-2 signaling. While the STAT5 serine kinase is unknown, the STAT3 proteins are phosphorylated in response to MAP kinase signaling. The sites of IL-2-regulated phosphorylation in (murine) IL-2R, SHC1 (isoform 2), STAT5A, and STAT5B are annotated where positions have been mapped. (b) Metabolic pathways activated downstream of IL-2R. IL-2 sustains the expression of MYC and activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) and the hypoxia inducible factor 1 transcriptional complex (HIF1α/HIF1β) to maintain the uptake of nutrients such as iron and glucose. IL-2 also sustains the expression of the amino acid transporter SLC7A5, which transports many of the essential amino acids, such as leucine, into cells. Amino acids are required to sustain mTORC1 activity and fuel translation. Glucose metabolism, via glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation (OxPhos), sustains ATP generation, and high ATP:ADP and ATP:AMP ratios, thus preventing the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which inhibits mTORC1. Protein synthesis is essential for maintaining the expression of proteins, such as MYC, with high turnover rates. Through the mTORC1 pathway, IL-2 can also sustain glycolytic metabolism and other biosynthesis in cytotoxic T lymphocytes to support cell proliferation, growth, and the expression of effector molecules.