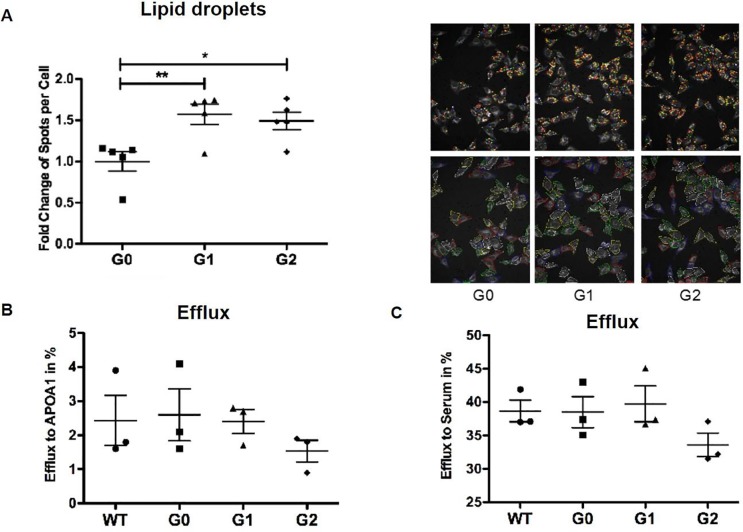
Fig 7. APOL1 risk variant expression in HeLa cells leads to lipid accumulation in the absence of decreased cholesterol efflux.
HeLa cells were infected with different APOL1 alleles using a lentiviral system. (A) HeLa cells were fixed and stained with BODIPY 493/503 and cell-mask blue. The number of lipid droplets per cell was determined by high throughput Perkin Elmer OPERA analysis and Acapella Image Analysis software. Dot blot analysis indicating a significantly increased number of Bodipy493/503-positive lipid droplets per cell in HeLa cells infected with APOL1 G1 or APOL1 G2 risk variants when compared to APOL1 G0 transfected HeLa cells (left). Representative images of Bodipy493/503 staining (right, upper panel) to identify lipid droplets and cell-mask staining (right, lower panel) to identify individual cells. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (B,C) HeLa cells expressing the different APOL1 alleles were labeled with 1 μCi/ml 3H-cholesterol in medium with 1% FBS for 24 hours, then washed with PBS, incubated in RPMI containing 2% human serum for 6 hours. Dot plot analysis indicating no changes in cholesterol efflux to APOA1 (B) or human serum (C) in APOL1 G1 and APOL1 G2 risk variant expressing HeLa compared to APOL1 G0 expressing cells. Both APOL1-G1 and APOL1-G2 HeLa cells showed increased lipid droplets compard to APOL1-G0 HeLa cells. There were no statistically significant differences in cholesterol efflux that were detected in this system.