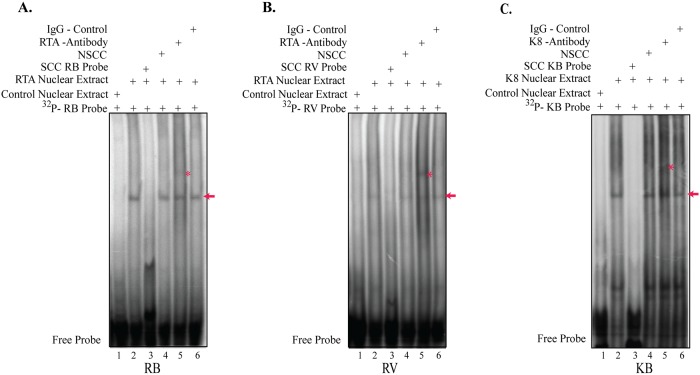
Fig 4. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) showing K-RTA and K8 binding to the novel sequence motifs.
(A) EMSA showing K-RTA binding to the RB motif. EMSA was performed using 32P-labeled double-stranded K-RTA binding RB sequence probe with control nuclear extract (lane 1) or K-RTA nuclear extract showing binding to RB probe (lane 2), 200x specific cold competitor RB probe (SCC, lane 3); RB probe with 200x non-specific cold competitor GFP probe (NSCC, lane 4), K-RTA binding to RB probe along with specific antibody against K-RTA showing a super-shift (lane 5), and RB probe with control antibody which does not affect the K-RTA binding to RB probe (lane 6). (B) EMSA showing K-RTA binding to the RV motif. EMSA was performed using 32P-labeled double-stranded K-RTA binding RV sequence probe with control nuclear extract (lane 1) or K-RTA nuclear extract showing binding to RV probe (lane 2), 200x specific cold competitor RV probe (SCC, lane 3), RB probe with 200x non-specific cold competitor GFP probe (NSCC, lane 4), K-RTA binding to RV probe along with specific antibody against K-RTA showing a super-shift (lane 5), and K-RTA binding to RV probe along with control antibody which does not affect the K-RTA binding to RV probe (lane 6). (C) EMSA showing K8 binding to the KB motif. EMSA was performed using 32P-labeled double-stranded K8 binding KB sequence probe with control nuclear extract (lane 1), or K8 nuclear extract showing binding to KB probe (lane 2), 200x specific cold competitor KB probe (SCC, lane 3), KB probe with 200x non-specific cold competitor GFP probe (NSCC, lane 4), K8 binding to KB probe along with specific antibody against K8 showing a super-shift (lane 5), and K8 binding to KB probe along with control antibody which does not affect the K8 binding to KB probe (lane 6).