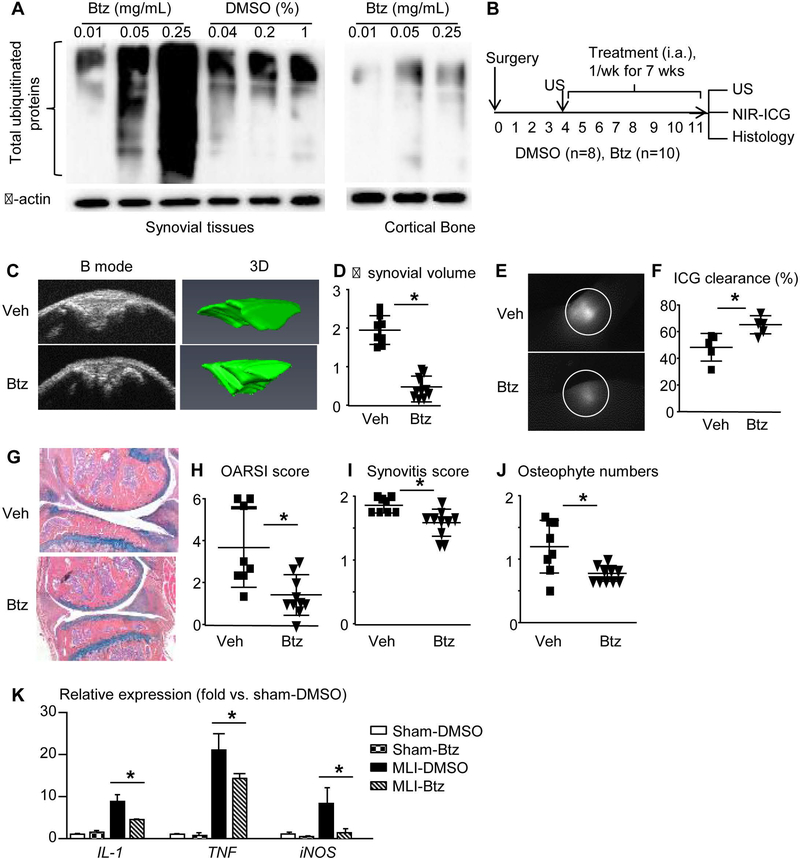
Figure 6. Bortezomib attenuates tissue damage in PTOA joints, improves synovial lymphatic function, and reduces LEC inflammation.
(A) WT mice were used. Different doses of Btz or 1% DMSO (Veh) were i.a. injected to knee joint. Levels of total ubiquitinated proteins in synovial tissues were examined by Western blot at 4 hours post-injection. Cortical bone from femur of the same joint was used as a control. (B) Schematic illustration of the experimental design in which WT C57BL/6J mice received MLI surgery, and 4 weeks later were randomized to DMSO or Btz (1× per week intraarticular injection for 7 weeks). (C) Ultrasound images of B-mode and 3D reconstruction indicate synovial volume at the end of treatment. (D) Changes of synovial volume (mm3) pre- and post-treatment. (E) ICG signal intensity of knee joints 6 hours post-ICG administration. (F) ICG clearance (%). (G) AB/OG stained sections. (H-J) OARSI score, synovitis score, and osteophyte numbers. Data are mean + SD. n=8–10 mice/group. Unpaired t test. *p<0.05. (H) LECs from synovium pooled from 4 joints were subjected to qPCR. Data are mean + SD. n=3 repeats. The fold-changes were calculated using samples from sham-Veh group as 1. Unpaired t test. *p<0.05