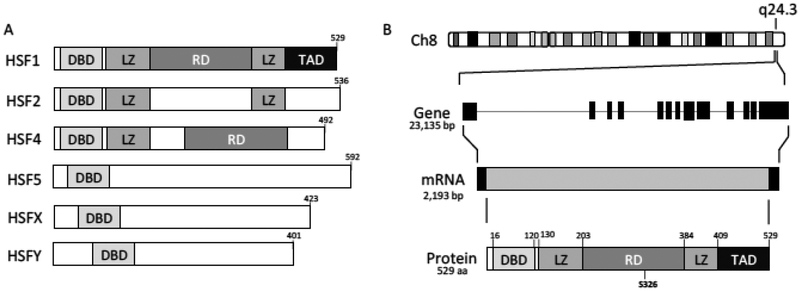
Fig. (1).
Heat Shock Factor 1 (HSF1) Gene. A) There are six human HSF isoforms all containing a homologous DNA binding domain recognizing the heat shock element (HSE). B) HSF1 is located on the long arm of chromosome 8 at q24.3. The resulting gene has 13 exons with a full gene size of 23,135 bp that transcribes to an mRNA of 2,193 bp. The resulting protein is 529 aa and has multiple functional domains. The DNA binding domain (DBD) is a winged helix-turn-helix domain. The leucine zipper (LZ) domains mediate the trimerization of HSF1 upon activation. The regulatory domain is home to many post-translational modifications that appear to regulate HSF1 transcriptional activity with Ser326 seemingly the key phosphorylation necessary for activity. The transactivation domain (TAD) of HSF1 recruits p-TEFb to release proximal promoter pausing and promote transcription elongation of target genes.