Fig. 1.
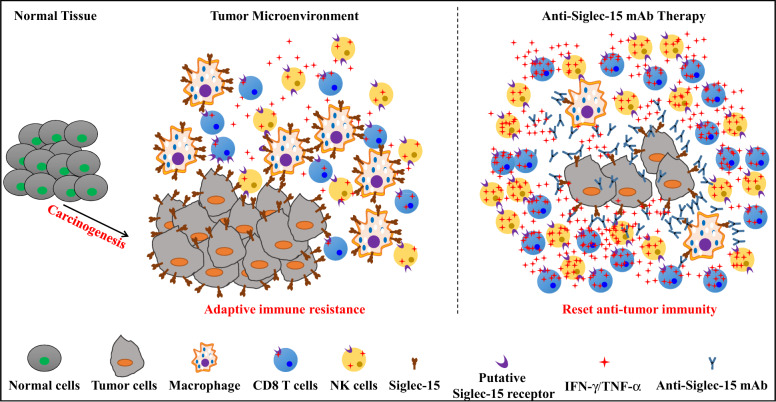
Siglec-15 is a candidate target for normalization cancer immunotherapy. Siglec-15 is minimally expressed on normal tissues at steady-state. However, the expression of Siglec-15 is redundant in a broad spectrum of human cancers and tumor associated myeloid cells. Interestingly, Siglec-15 is mutually exclusive to B7-H1 in human non-small cell lung cancer, which may partially due to its induction by M-GSF and suppression by IFN-γ. Siglec-15 engages with a putative responder protein expressed on effector cells such as CD8 T cells, which induces subsequent suppression of anti-tumor immune responses. Blocking Siglec-15 amplifies anti-tumor immunity in the tumor microenvironment and inhibits tumor growth