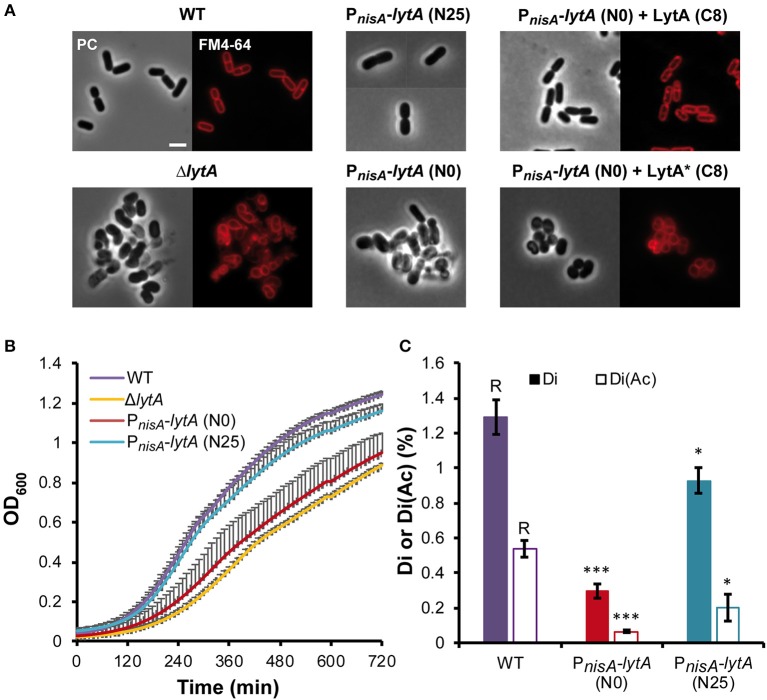
Figure 2.
Effect of LytA deficiency on cell morphology, growth, and PG composition. (A) Images of L. plantarum cells obtained by phase contrast (PC) microscopy and epifluorescence microscopy for membrane labeling with FM4-64. Left panel, WT and ΔlytA mutant; middle panel, conditional PnisA-lytA mutant without (N0) or with nisin 25 ng ml−1 (N25); right panel, complementation of PnisA-lytA mutant with LytA (Pshp0064-lytA; + LytA) and a catalytic mutant of LytA (Pshp0064-lytA*; + LytA*), grown without nisin (N0) in presence of ComS (8 μM, C8). Cells were collected in exponential phase from MRS cultures (with chloramphenicol when needed) and observed on agarose pads after suspension in PBS. Similar observations were obtained from at least 3 independent experiments. The scale bar is 2 μm. (B) Growth curves of WT, ΔlytA mutant, and PnisA-lytA mutant (N0 and N25) in MRS medium. Curves were generated from triplicates (mean values + standard deviations). (C) Percentage of disaccharides-dipeptides without and with O-acetylation (Di and Di+Ac, respectively) in the PG of WT and PnisA-lytA mutant (N0 and N25) after mutanolysin digestion. Mean values of three independent extractions ± standard deviations. Significance with respect to the WT (R, reference) is based on Student's t-test. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001, respectively.