Figure 8.
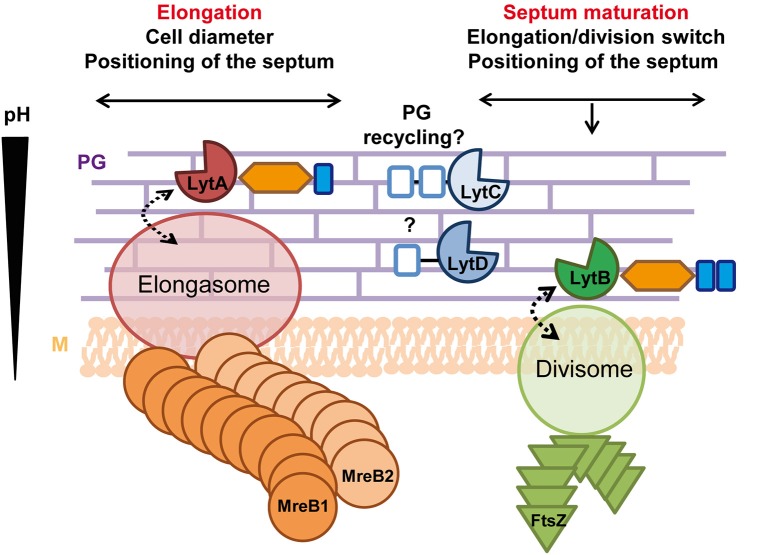
Roles of LytA and LytB in the cell cycle. LytA is mainly involved in cell elongation and in the control of cell diameter. Its absence (probably indirectly) also affects septum positioning. LytA potentially interacts with the elongasome and its basophilic LysM domain suggests that LytA could act in the external PG layers where the pH is higher. LytB is implicated in division (timing, septum maturation, and lateral positioning) and potentially interacts with the divisome. The presence of two acidophilic LysM domains suggests that LytB could be localized close to the cell membrane where the pH is lower. LytC is proposed to be involved in the recycling/catabolism of PG stem peptides while LytD could be an accessory endopeptidase unrelated to the cell cycle. Labeling of accessory domains of Lyt enzymes are as in Figure 1. Dotted arrows indicate potential interactions. PG, peptidoglycan; M, cytoplasmic membrane.