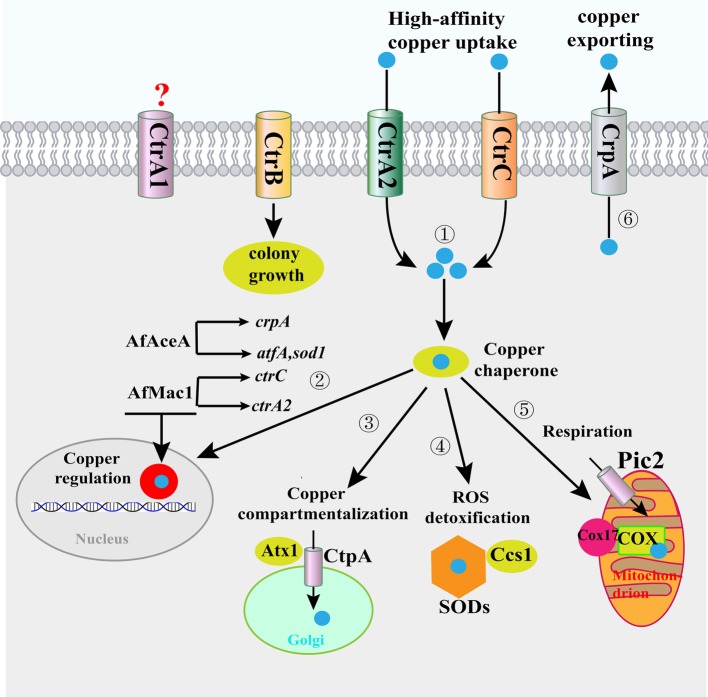
Figure 1.
Copper homeostasis mechanisms in A. fumigatus. ① High-affinity copper transporters at the plasma membrane participate in copper (blue spheres) transport from the extracellular environment to the intracellular environment. ② In the cytoplasm, copper is bound by copper chaperones that facilitate the delivery of copper to the nucleus for copper homeostasis regulation; AfMac1 induces the ctrC and ctrA2 genes to respond to low copper, and AfAceA induces the expression of the copper extrusion pump CrpA, as well as the ROS detoxification proteins AtfA and SOD1, in response to excess copper. ③ In the cytoplasm, copper is bound by copper chaperones that facilitate the delivery of copper to subcellular compartments (i.e., the Golgi complex) for storage or ④⑤ cytoplasmic and mitochondrial enzymes for functional activation. Parts 3, 4, and 5 are not proven in A. fumigatus, only in S. cerevisiae. ⑥ When the concentration of copper in the cytoplasm exceeds the homeostatic capacity, A. fumigatus employs efflux to detoxify excess copper. Abbreviations: SOD, superoxide dismutase; ROS, reactive oxygen species.