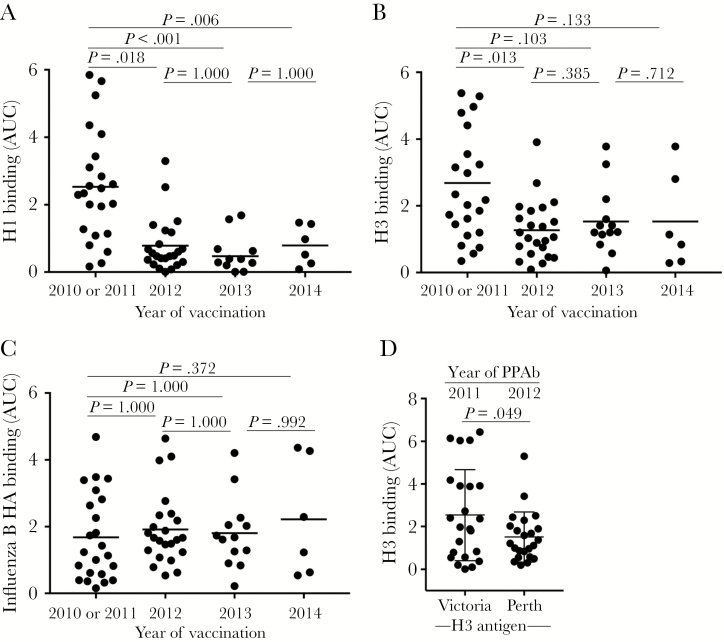
Figure 3.
Hemagglutinin (HA)–specific plasmablast-derived polyclonal antibody (PPAb) responses after repeated trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine (TIV) receipt. The immunoglobulin G (IgG) binding reactivity against recombinant HA protein was analyzed by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), using PPAbs serially diluted 10-fold, from 1:100 to 1:100 000. The area under the curve (AUC) was calculated to represent the reactivity of each PPAb sample. A, PPAb reactivity against the recombinant H1 protein of the A/California/7/2009 (H1N1) strain, which remained unchanged for the 2010–2014 TIV formulation (Table 2). B, PPAb reactivity against the recombinant H3 protein derived from the influenza A(H3N2) virus component of TIV for each respective season, which changed in 2012 and 2014 (Table 2). C, PPAb reactivity against the recombinant HA protein derived from the influenza B virus component of TIV for each respective season, which changed in 2012 and 2013 (Table 2). In panels A–C, the horizontal bars indicate means of AUCs. P values for pairs of compared means are adjusted for multiple comparisons and marked within each graph. See Supplementary Figures 3, 6–9, and 13 for details of statistical analysis for panels A–C. D, PPAb reactivity in 2010 or 2011 and in 2012 against the conserved epitopes on the 2 H3 proteins derived from the influenza A(H3N2) virus components in TIV during these years. The strain of the testing H3 antigen is indicated under the graph. The means and standard deviations are indicated with horizontal bars and vertical brackets. A paired 2-tailed t test was used to compare the means.