Table 1.
In vitro activity of the target compounds 6–16, 18c, and 21 against eEF-2K.
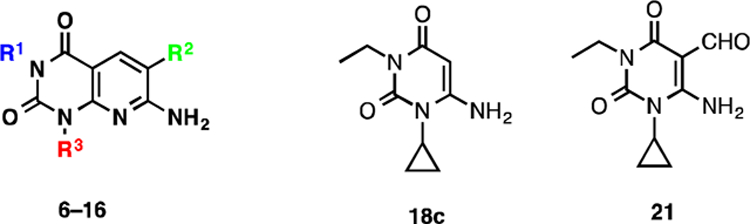 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | IC50 (MM) |
| 7 | H | CONH2 | cyclopropyl | 6.6 ± 0.2 |
| 8 | Me | CONH2 | cyclopropyl | 6.1 ± 0.2 |
| 6 | Et | CONH2 | cyclopropyl | 0.42 ± 0.01 |
| 9 | n-Pr | CONH2 | cyclopropyl | 0.93 ± 0.03 |
| 10 | CH2-Ph-NO2-p | CONH2 | cyclopropyl | >25 |
| 11 | CH2-Ph-NH2-p | CONH2 | cyclopropyl | >25 |
| 12 | Et | CSNH2 | cyclopropyl | >25 |
| 13 | Et | CO2Et | cyclopropyl | >25 |
| 14 | Et | CN | cyclopropyl | >25 |
| 15 | Et | CONH2 | Et | 1–2 |
| 16 | Me | CONH2 | Me | >25 |
| 18c | - | - | - | >25 |
| 21 | - | - | - | >25 |
Inhibitor dose response assays were performed with 5 nM recombinant eEF-2K enzyme at various concentrations of the inhibitor, in the presence of 50 μM free Ca2+, 200 nM CaM and 10 μM [γ−32P]ATP, against 150 μM peptide substrate as described under the experimental section. The inhibitor was incubated with eEF-2K for 30 min at 30 °C before initiating the assay with peptide and [γ−32P]ATP. Kinase activity in each case was determined by calculating the rate of phosphorylation of the peptide (μM/s), and dose-response curves for data conforming to inhibition were fit to equation 1.
