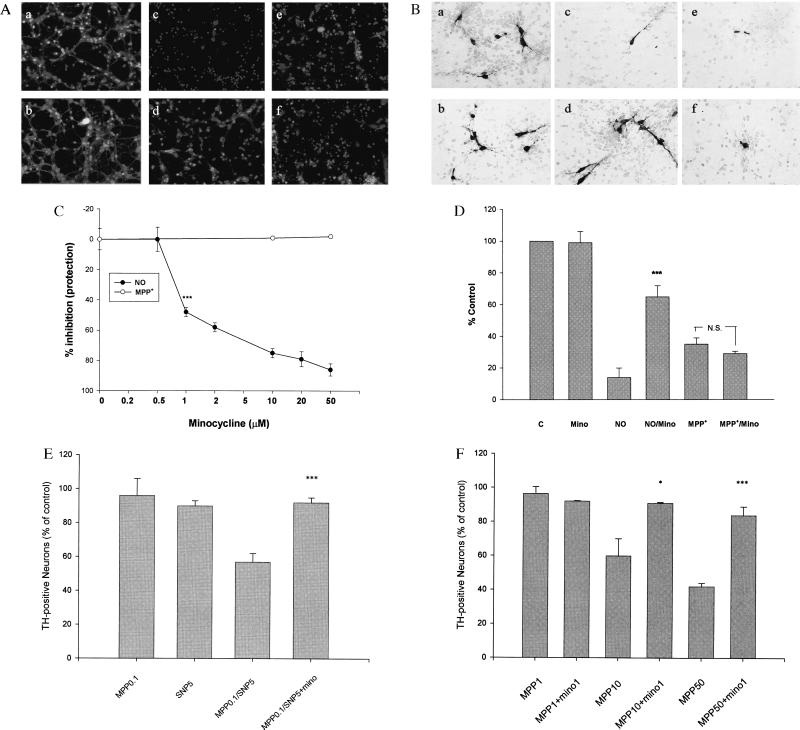
Figure 4.
Effects of minocycline on NO and MPP+ toxicity of cultured CGN and RMN. (A) Minocycline blocks NO-induced neuronal death of CGN, but not MPP+-induced neurotoxicity. CGN were exposed to increasing concentrations of minocycline (0.5–50 μM) for 24 h in the presence of SNP (50 μM, 24 h) or MPP+ (70 μM, 72 h). Viable and dead CGN were quantified by using fluorescein diacetate (yellow-green) and propidium iodide (red) staining as described (22). (a–f) Representative fields of CGN were photographed (×100) after double staining in the absence (a, c, and e) or presence (b, d, and f) of minocycline (20 μM). (a and b) No treatment. (c and d) SNP treatment. (e and f) MPP+ treatment. (C) Quantification of the effects of minocycline on MPP+-treated CGN. Values are expressed as a % of control (untreated) cultures for each concentration of minocycline. Data represent the mean ± SE (bars) values of triplicate determinations from a single but representative experiment repeated three times with similar results (***, P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA; N.S., not significant). (B) Minocycline blocks NO-induced neuronal death of cultured RMN but not MPP+-induced neurotoxicity. (a–f) Representative fields of fetal RMN (20) were photographed (×200) after TH staining (see text for details). Compare untreated control and minocycline-treated cultures (a and b) with those exposed to 10 μM SNP (NO) (c) or 10 μM MPP+ (e) plus minocycline (10 μM) (d and f). Note that minocycline markedly attenuates NO neurotoxicity (d), but not MPP+ neurotoxicity (f). (D) Quantification of the effects of minocycline on SNP (10 μM) and MPP+ (10 μM)-treated fetal rat RMN. TH-positive cells were counted from photomicrographs like those shown in B above. Data are from a representative experiment repeated twice with similar results (***, P < 0.001 compared with NO alone). (E) Minocycline blocks combined NO/MPP+ toxicity of cultured CGN. Quantification of the effects of minocycline on both SNP (5 μM) and MPP+ (0.1 μM)-treated CGN. Data are from a representative experiment repeated three times with similar results [***, P < 0.001 compared with SNP (5 μM) and MPP+ (0.1 μM) alone]. (F) Minocycline blocks MPP+ neurotoxicity in neuron/glia cocultures. Quantification of the effects of minocycline on MPP+ (1–50 μM)-treated fetal rat RMN/glia cocultures (24). TH-positive cells were quantified from photomicrographs like those shown in B above. Note that in the presence of glia higher concentrations of MPP+ are required to kill dopamine neurons. Nonetheless, in the presence of glia the neurotoxic effects of MPP+ are completely blocked by minocycline. Data are from a representative experiment repeated twice with similar results. (*, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001 compared with MPP+ alone).