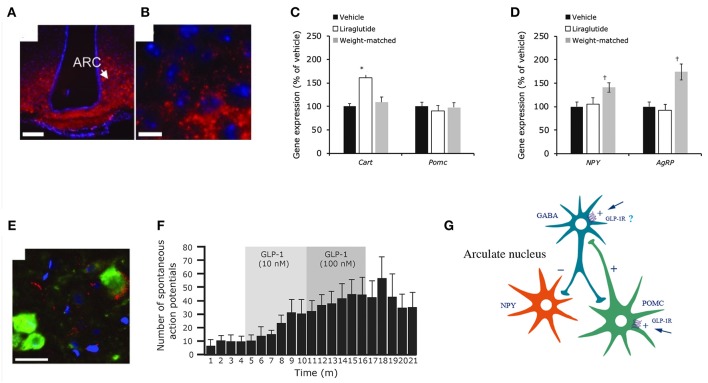
Figure 8.
Liraglutide and the mouse brain. Distribution of liraglutide594 or exendin(9-39)594 in brain. (A,B) liraglutide594 had access to ARC, in which it bound the GLP-1R and internalized. (B) High-magnification image showed that liraglutide594 was internalized and the fluorescent signal was located in the cytoplasm. Staining, Hoechst nuclear stain (blue) and liraglutide594/exendin(9-39)594(red). Scale bars: 100 μm. Liraglutide treatment regulates ARC gene expression and ARC neuronal activity. (C) Liraglutide treatment for 28 days in DIO rats significantly increased mean Cart mRNA levels in the ARC (*p < 0.001 liraglutide vs. vehicle and vs. weight matched), whereas Pomc expression was unaffected. (D) Npy and Agrp mRNA levels were significantly increased in weight-matched rats–but not following treatment with liraglutide (†p < 0.05 weight matched vs. vehicle and vs. liraglutide). Data are mean ± SEM, and statistical analyses were performed using 1-way ANOVA, with Fisher's post hoc test. Images (E,F) show neuronal accumulation and activity following GLP-1R simulation. Specifically, panel (E) shows CART- and liraglutide594-positive cells shown as mean ± SEM. Staining, Hoechst nuclear strain (blue), liraglutide594 (red) and CART (green). Scale bar: 25 μm. Panel (F) shows the effects of GLP-1(7-36)amide on firing rate of spontaneous action potentials in POMC/CART neurons. (G) Proposed regulation of neuronal activation by liraglutide. Summary diagram demonstrating the suggested regulatory pathway of GLP-1 on ARC NPY and POMC neurons. GLP-1 stimulates POMC neurons directly through the GLP-1R and is suggested to indirectly inhibit ARC-NPY neurons through a local inhibitory GABA neuron. ANOVA, analysis of variance; ARC, arcuate nucleus; CART, cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript; DIO, diabetes induced obesity; GABA, gamma-amino butyric acid; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1; GLP-1R, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; NYP, neuropeptide Y; POMC, proopiomelanocortin; SEM, standard error of the mean; veh, vehicle. Republished with permission of American Society For Clinical Investigation, from Secher et al. (117), Copyright 2018; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.