Figure 10.
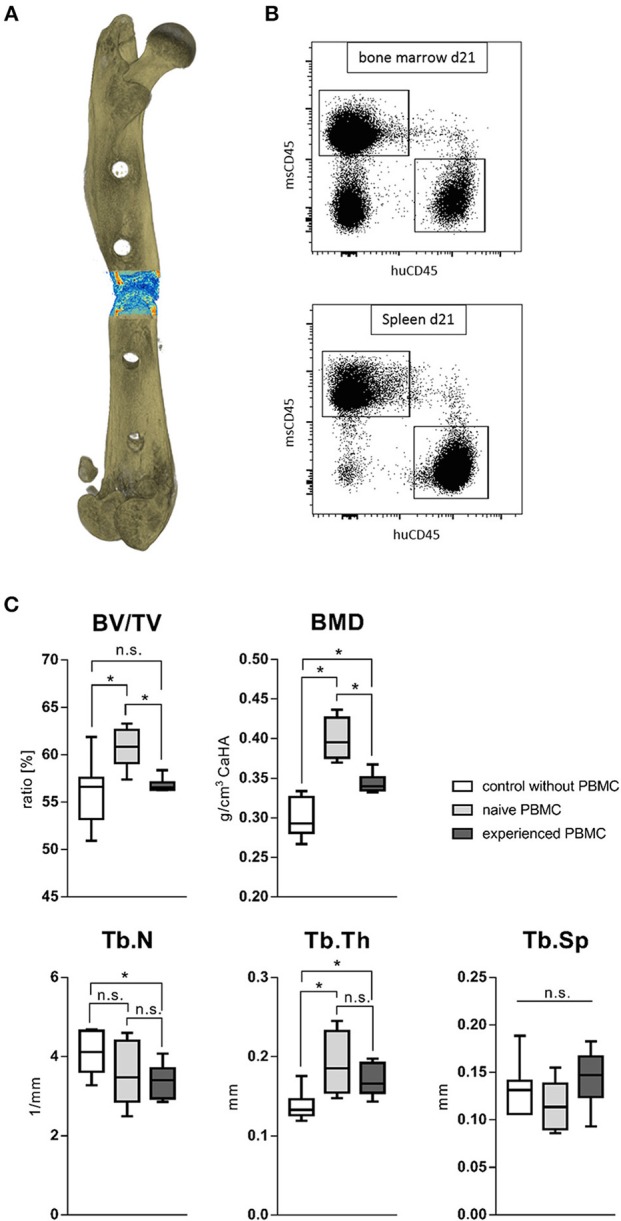
Fracture healing outcome of humanized PBMC mice. (A) Representative image of a 21 days old fracture gap. (B) Human immune cells settled to spleen and bone marrow in significant levels after transfer. (C) Healing under the influence of either experienced or more naïve peripheral blood mononuclear cells (hPBMC) showed a beneficial effect of a more naïve immune phenotype. The bone volume in total volume (BV/TV) was significantly increased under the influence of more naïve hPBMC compared to the control without hPBMC and more experienced hPBMC. The bone mineral density (BMD) and trabecular thickness (Tb.Th) stood to benefit from immune cells. The more naïve hPBMC further increased the mineral density within the fracture gap compared to more experienced hPBMC. The number of newly formed trabecular structures (Tb.N) seemed to decrease under the influence of more experienced hPBMC. N = 6 animals in the naïve hPBMC group, N = 8 each in control and experienced hPBMC group, boxplot distribution with median, Mann-Whitney U-test, *p < 0.05.
