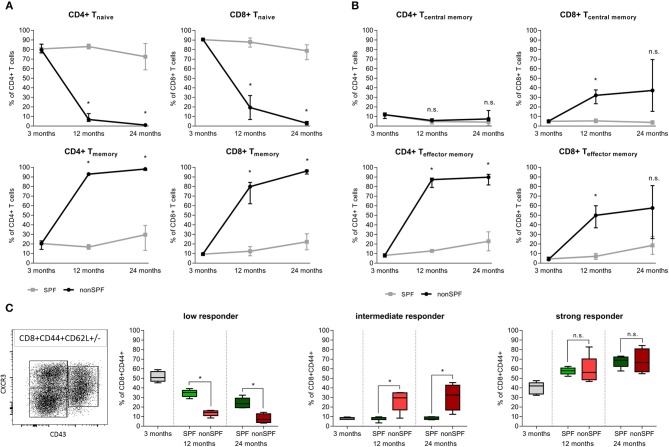
Figure 2.
Adaptive immunity changes level of experience among housing conditions (SPF vs. non-SPF) and aging. (A) Naïve level of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells diminished and the memory level increased with aging. Exposing the animals to antigens boosts the memory formation significantly. (B) Classification of T cells into central memory (TCM) and effector memory (TEM) revealed a different picture for CD4+ and CD8+ T cells: CD8+ T cells increased both compartments under non-SPF conditions, whereas the CD4+ central memory T cells were constant among ages and housing conditions. Keeping mice under SPF conditions oppressed the effect of memory formation. (C) CD8+ memory T cells differ in the recall efficiency after antigen encounter. Strong responder CD8+ memory T cells were not affected by non-SPF housing, whereas intermediate responder could only be found under non-SPF conditions (intermediate responder are proven to show fast proliferation and vast cytokine production). The low responder fraction diminished further under non-SPF conditions compared to SPF housing. N = 6 animals per age group and housing conditions, (A,B) shows median with interquartile range, (C) shows boxplot distribution with median, Mann Whitney U-test, *p < 0.05.