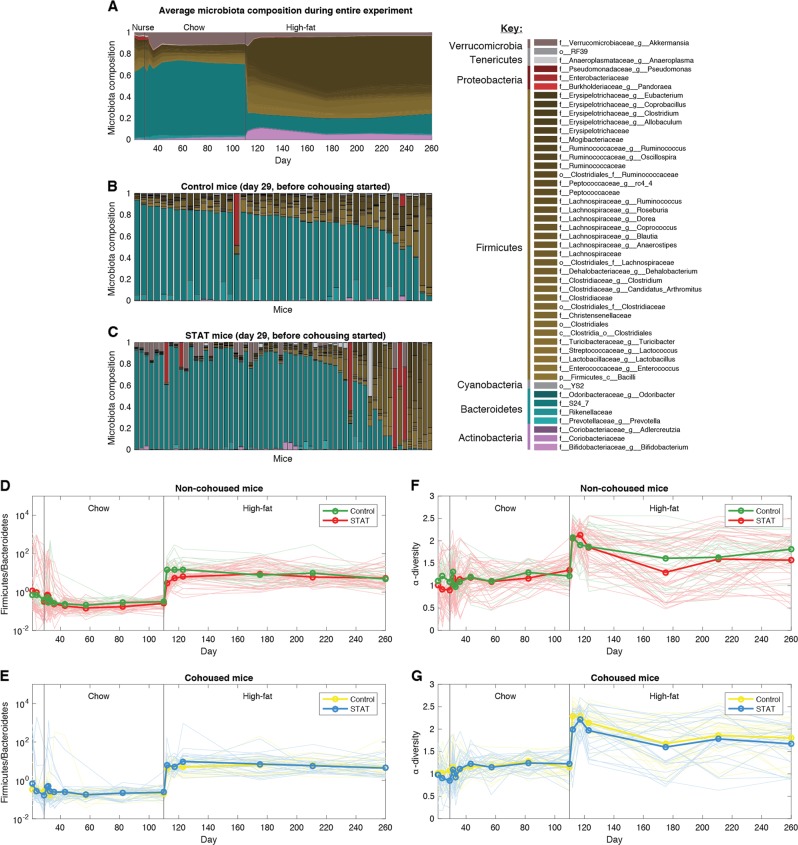
Fig. 4.
The shift to high-fat diet increased Firmicutes and α-diversity, and had the strongest impact on microbiota composition. a The average composition across all mice changed from a microbiota dominated by Bacteroidetes (in blue) to one dominated by Firmicutes (in brown). b, c The compositions in each mice at the last day of nursing, before the cohousing started. The Control and STAT mice are ranked, from left to right, by their ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes. d, e Ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes, a quantity previously linked to high-fat diet and obesity, increased in high-fat diet, but STAT had no significant impact. f, g The α-diversity (calculated using the Shannon index) also increased when high-fat diet was begun but STAT had no significant impact