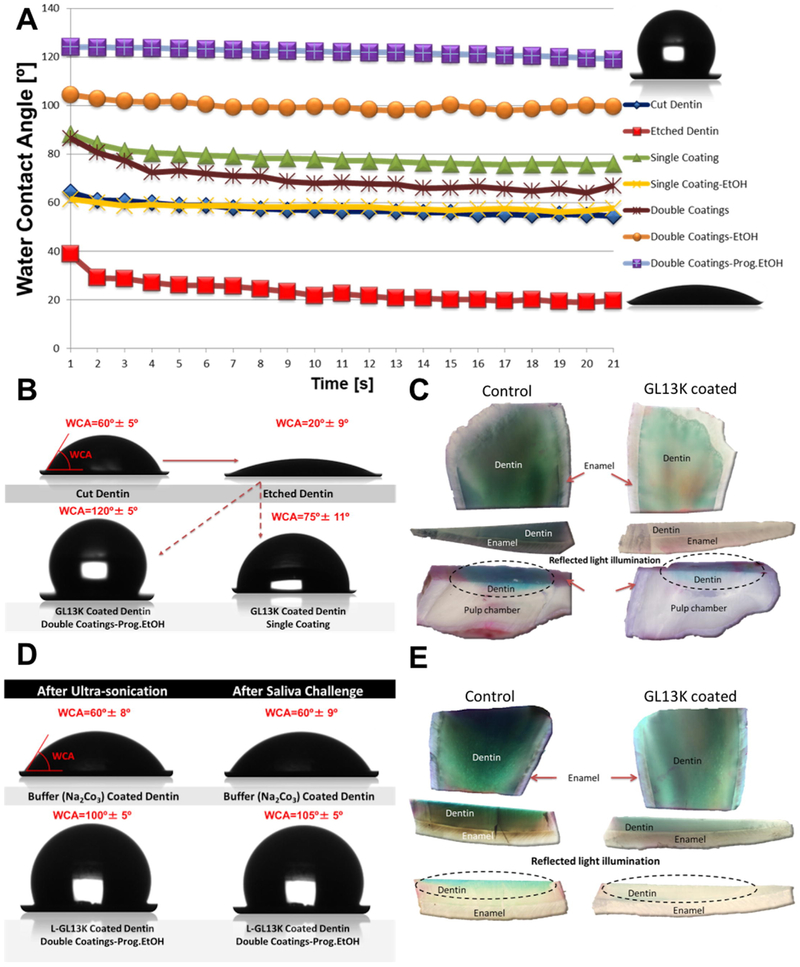
Figure 4. Hydrophobic dentin and its impermeability before and after chemical, mechanical and saliva-mediated challenges.
A) Dynamic water contact angles (WCA, average value, n=7) for cut and etched bovine dentin (controls) and dentin treated with amphipathic peptides following different protocols (see materials and methods section for description of the different dentin treatments); B) sessile water drop images and final WCA (average ± standard deviation, n=7) on bovine dentin before (cut and etched) and after peptide treatments; C) dentin impermeability: copper sulfate acidic dye penetration at the superficial and pulp overlaying dentin visualized using transmitted or reflected light illumination; D) sessile water drop images and final WCA (average ± standard deviation, n=5) on buffer treated and peptide coated bovine dentin, before and after ultrasonication and saliva challenges, E) dentin impermeability after saliva-mediated challenges: copper sulfate dye penetration through dentin visualized using transmitted or reflected light illumination.