FIGURE 1.
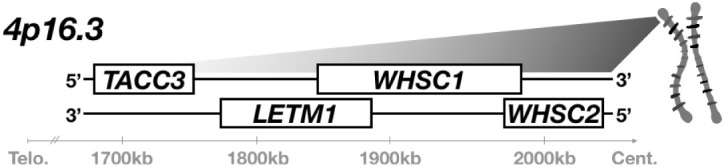
WHS is typically caused by heterozygous microdeletion of numerous genes within 4p16.3. A segment of this region is illustrated here. A microdeletion that spans at least WHSC1, WHSC2, and LETM1 is currently assumed to be necessary for full WHS diagnostic presentation; children affected by the disorder often possess larger deletions that extend further telomeric and impact additional genes, such as TACC3.
