Figure 3: Comparative proteomics reveals that flavivirus NS5 antagonizes host restriction factor PAF1C.
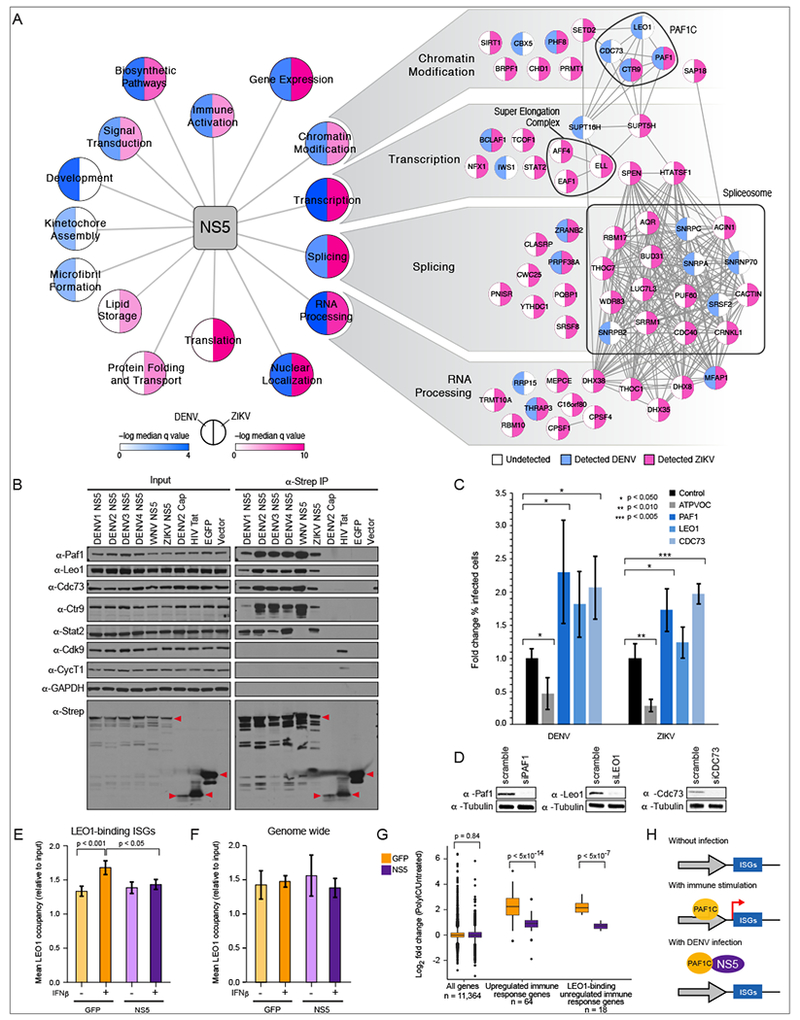
(A) DENV-human (blue) and ZIKV-human (pink) data were compared using gene ontology biological process and cellular compartment categories. Highly similar categories with significant enrichment (FDR corrected q value < 0.05) were combined (Table S5), and median q values of combined terms are plotted. Individual interactions detected in DENV (blue) and ZIKV (pink) datasets are shown for a subset of NS5 enrichment categories. (B) NS5 interaction with PAF1C subunits is conserved across flaviviruses. 2xStrep II tagged NS5 constructs were subjected to AP and Western blot. Stat2 is a positive control for NS5 AP, DENV Cap (Capsid), HIV Tat and EGFP are negative controls. Red triangles indicate band corresponding to bait. (C) Knockdown of PAF1C subunits leads to increased infectivity by DENV and ZIKV. Error bars reflect standard deviation of four replicates. P values were calculated using a paired, one tailed student’s t-test. (D) Knockdown of PAF1C components was confirmed by Western blot. (E) Mean LEO1 occupancy for 67 DENV-induced genes plotted for ChIP-seq triplicates. Error bars reflect standard deviation. P values were calculated using paired, two-tailed Mann-Whitney U-test. (F) NS5 inhibition of LEO1 recruitment is specific to ISGs. (G) Quantitative comparison of genes expressed in NS5- and GFP-expressing cells after immunostimulation. Left side: genome-wide (11,364 genes); Middle: 64 genes differentially regulated by polyIC; Right: Overlap of genes from set of 64 genes in middle panel and the genes whose binding of LEO1 is affected by NS5 (18 genes). (H) Model of NS5 effect on immune response gene expression through interaction with PAF1C.
