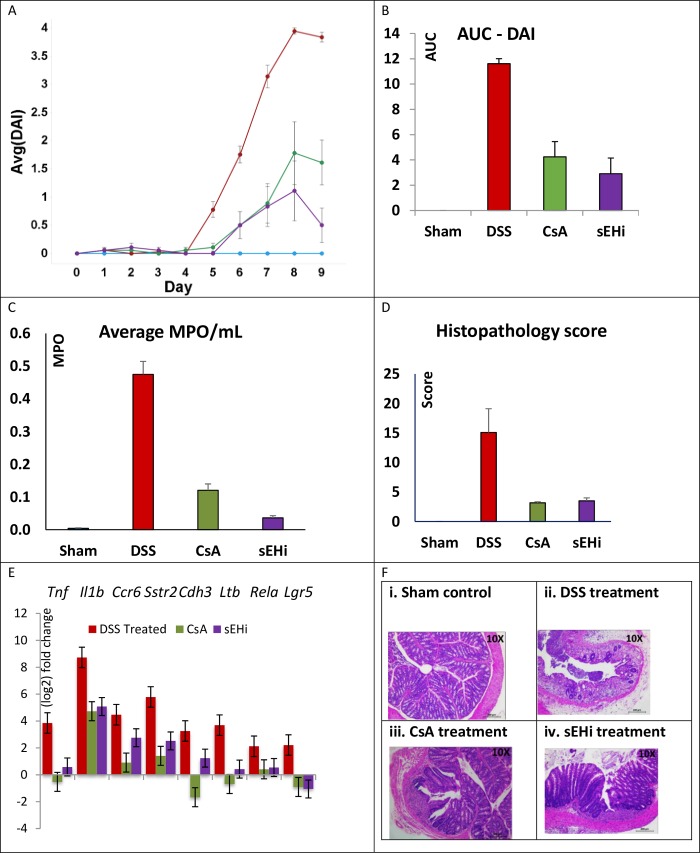
Fig 2. DSS-induced colitis mouse model.
DSS-induced colitis is a common in vivo model for IBD. Our study employed acute dosing of DSS from Day 0 to Day 5. Compound treatments were from Day 0 to Day 9. Experimental groups were: Sham = vehicle control (no DSS or other treatment, n = 6), DSS = DSS-only (n = 12), CsA = 10 mg/kg i.p. treatment (n = 6), EPHX2i = GSK1910364A 50 mg/kg orally, twice daily (n = 6). (A) Mean DAI is plotted versus time; error bars reflect standard errors. (B) AUC values for each group were calculated at experiment conclusion. Sample sizes for each group are the same as in (A). Both CsA and EPHX2i significantly decreased the AUC compared to DSS-only control (ANOVA P-value < 0.05). (C) MPO protein expression is used as a surrogate biomarker for inflammation. MPO was nearly absent in the sham control mice, but levels were significantly increased in the DSS-treated animals. Both cyclosporine and EPHX2i treatment significantly decrease MPO expression, with EPHX2i showing a return to near normal level. (D) The histopathology scoring system is given in Table 2. DSS-treatment significantly increased the score, compared to vehicle control group. Both CsA and EPHX2i treatment significantly decrease the histopathology score by similar amount. (E) RT-PCR measurement of selected marker gene mRNA expression. All expression values were normalized to the levels in the vehicle control group. For most marker genes, DSS-treatment caused large increases/decreases in mRNA levels. Both CsA and EPHX2i treatment tended to restore expression levels back toward baseline (Il1b, Ccr6, Sstr2, Lgr5) or to near baseline levels (Tnf, Ltb, Rela). (F) H&E staining of selected colonic tissue sections from DSS-mice. 10x magnification of representative colon sections from each of the four treatments groups. (i) the sham control shows normal histology. (ii) the DSS-control shows widespread damage. (iii) CsA and (iv) EPHX2i treatment both show substantial protection from DSS-induced damage.