Fig 7. Summary of EPHX2i and knockout in mouse models and human disease explants.
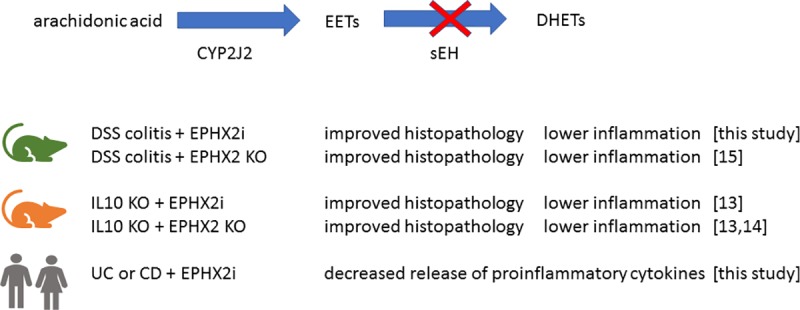
Similar protective effects on histology and inflammation were observed whether EPHX2 was decreased using chemical inhibitors or due to genetic deficiency. This was the case for both DSS-induced colitis and IL10 knockout mouse models. In colon explants from human patients, EPHX2i decreased production of inflammatory cytokines, compared to DMSO controls. This effect was seen in both UC and CD patient tissue.
