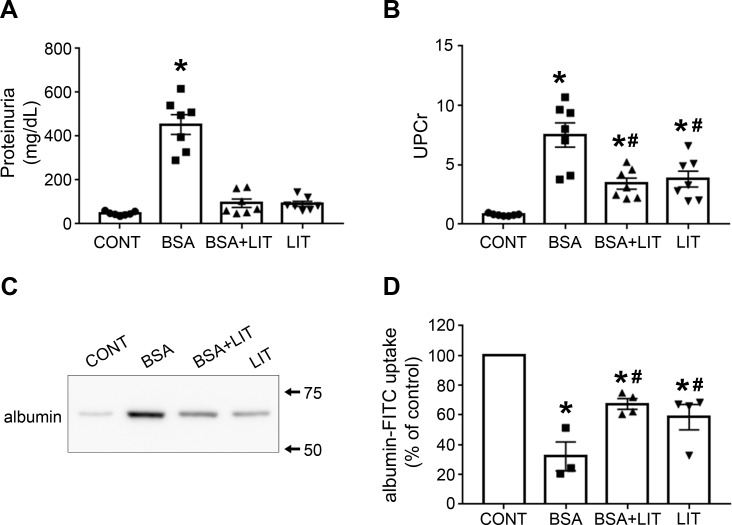
Fig 1. Lithium treatment reduces proteinuria induced by albumin overload due to the increase in albumin reabsorption.
Male BALB/C mice were separated into different experimental groups as described in the Materials and methods section. CONT, control group; BSA, group that received intraperitoneal injections 10 g/kg/day BSA for 7 days; BSA+LIT, group that simultaneously received BSA injection and 300 mg/kg/day lithium carbonate via gavage; LIT, lithium-treated group. A) Proteinuria (n = 7). B) Ratio of urinary protein and urinary creatinine (UPCr; n = 7). C) Urinary albumin content was assessed by immunoblotting. Urinary volume was adjusted for 10 μg of urinary creatinine. D) In vivo albumin reabsorption (n = 4). Mice received a single intravenous dose of 5 μg/g BSA-FITC used as a tracer. After 15 min, the animals were perfused with saline and the BSA-specific fluorescence intensity in the renal cortex was determined. The results are expressed as means ± SE. *P < 0.05 versus CONT group; #P < 0.05 versus BSA group.