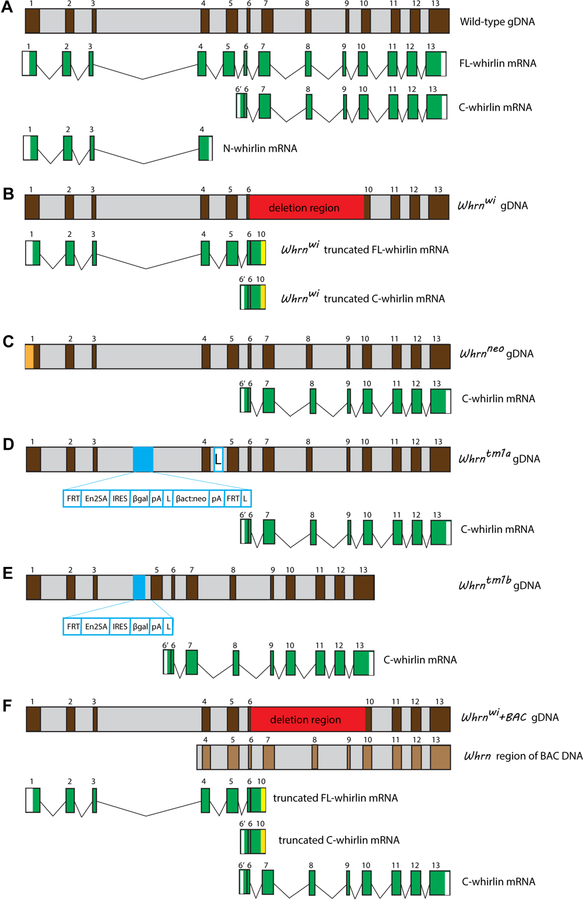
Figure 3:
Whrn genomic DNA and mRNA variants in wild-type and Whrn mutant mice. (A) FL-, N-, and C-terminal whirlin mRNA variants found in the wild-type mice. For simplicity, only one representative N-whirlin mRNA variant is shown, although several N-whirlin mRNA variants have been reported (Belyantseva et al., 2005; Ebrahim et al., 2016; Mathur et al., 2015b; Wright et al., 2012). In addition, the C-whirlin variants starting from exon 1 are not shown. (B) A deletion from exon 6 to exon 10 (red box) truncates both FL-whirlin mRNA and C-whirlin mRNA variants in Whrnwi mice. A vertical yellow bar indicates a premature stop in truncated Whrnwi mRNA fragments. N-whirlin mRNA variants were not found in our study, although they were found in the Whrnwi inner ear by Ebrahim et al. (Ebrahim et al., 2016; Mathur et al., 2015b; Mathur et al., 2015c). (C) Only a C-terminal whirlin variant is present in Whrnneo mice, which has a Neor cassette (orange box) in the 5′ region of exon 1. (D) A targeting cassette (light blue box) in intron 3 of Whrntm1a genomic DNA (gDNA) disrupts the FL-whirlin variant. However, it is expected that the C-terminal whirlin mRNA variant remains unaffected. L, loxP site. (E) Exon 4 and a part of the targeting cassette (light blue box) in Whrntm1a gDNA are deleted in Whrntm1b mice, which disrupts the FL-whirlin variant. The C-terminal whirlin mRNA variant is expected to be unaffected. (F) Whrnwi+BAC mice are expected to express C-terminal whirlin mRNA variant from the transgenic BAC DNA, in addition to the variants expressed in Whrnwi mice. Brown and light grey in the Whrn gDNA and BAC DNA denote the exons and introns, respectively, with exon numbers in Arabic numerals. White color denotes 5′ and 3′-untranslated regions, and green color denotes the coding sequence region of whirlin mRNA variants.