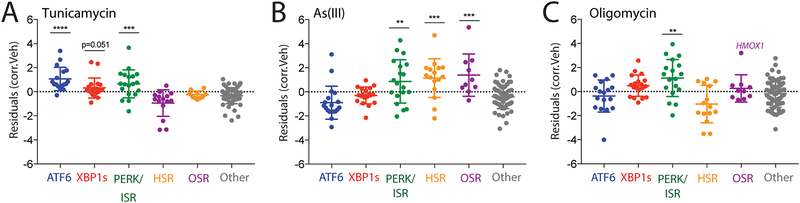
Figure 4. Targeted RNASeq profiling defines activation of stress-responsive signaling pathways induced by diverse environmental toxins.
A. Plot showing residuals calculated by comparing the expression of our stress-responsive gene panel between HEK293T cells following treatment with tunicamycin (Tm; 10 μM, 4 h) or vehicle. Calculation of residuals was performed as described in Fig. 2A. Genes are grouped by target stress-responsive signaling pathway. Statistics were calculated using one-way ANOVA, Significance shown reflects comparison to “Other” target transcript set. ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. See Table S3 for full ANOVA table.
B. Plot showing residuals calculated by comparing the expression of our stress-responsive gene panel between HEK293T cells following treatment with arsenite (As(III); 25 μM, 16 h) or vehicle. Calculation of residuals was performed as described in Fig. 2A. Genes are grouped by target stress-responsive signaling pathway. Statistics were calculated using one-way ANOVA, Significance shown reflects comparison to “Other” target transcript set. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. See Table S3 for full ANOVA table.
C. Plot showing residuals calculated by comparing the expression of our stress-responsive gene panel between HEK293T cells following treatment with oligomycin A (Oligo; 100 nM, 24 h) or vehicle. Calculation of residuals was performed as described in Fig. 2A. Genes are grouped by target stress-responsive signaling pathway. Statistics were calculated using one-way ANOVA, Significance shown reflects comparison to “Other” target transcript set. **p<0.01. See Table S3 for full ANOVA table.