Figure 8. PTBP2-regulated Shtn1L rescues Ptbp2−/− axonal length.
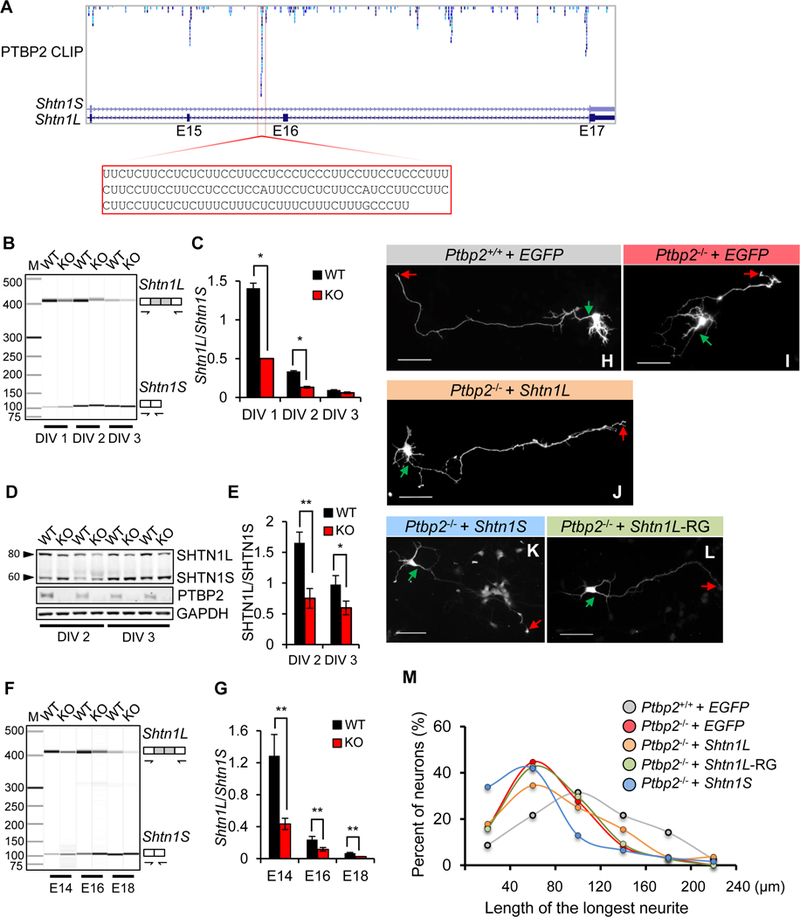
(A) Browser track of PTBP2 CLIP-Seq shows multiple PTBP2 binding sites in Shtn1 introns 14, 15, and 16. One prominent binding site is highlighted. (B-C) Alternative splicing of Shtn1 mRNA in WT and KO primary cortical neurons at DIV 1, 2, and 3. Data are represented as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. * p< 0.05, Student’s t-test. (D-E) A representative immunoblot demonstrating downregulation of SHTN1L protein in Ptbp2−/− primary cortical neurons. Data are represented as the mean ± SD. * p< 0.05, ** p< 0.01, Student’s t-test. (F-G) Representative virtual gel image of Shtn1 mRNA splicing in the WT and Ptbp2-KO neocortices at E14.5, E16.5 and E18.5. Data are represented as the mean ± SD. ** p< 0.01, Student’s t-test. (H-L) Representative images of Ptbp2+/+ neurons, Ptbp2−/− neurons, and Ptbp2−/− neurons transfected with Shtn1L-, Shtn1S-, or Shtn1L(RRR>GGG)-expressing plasmids. Shtn1L-RG indicates Shtn1L(RRR>GGG). Neurons were transfected at DIV1 and visualized by transfected GFP at DIV3. Green arrows indicate the starting sites of axons and red arrows the axonal tips. Scale bars: 25µm. (M) Density plot of Fig.8H-I shows the length distribution of the longest neurites (axons). Shtn1L, not Shtn1S or Shtn1L(RRR>GGG), partially rescues the defect of axonal length in Ptbp2−/− neurons. N=162 (Ptbp2+/+), 159 (Ptbp2−/−), 84 (Ptbp2−/− + Shtn1L), 108 (Ptbp2−/− + Shtn1L-RG) and 62 (Ptbp2−/− + Shtn1S) neurons from 4–7 biological replicates.
