Figure 4.
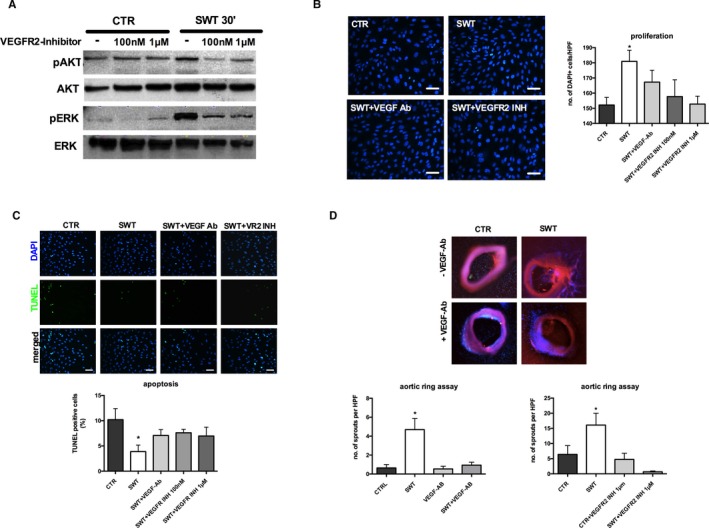
Shock wave effects depend on VEGF signaling. A, Activation of Akt and ERK is abolished upon VEGFR2 inhibition. Early phosphorylation of Akt as well as ERK after SWT was inhibited by pretreatment of cells with VEGFR2 inhibitor vandetanib. All experiments were performed at least in triplicate. B, SW‐induced endothelial cell proliferation is VEGFR2 dependent. HUVECs were pretreated with VEGF antibody or vandetanib and subsequently underwent SWT, and DAPI‐stained nuclei were quantified 24 h after treatment. VEGF inhibition and VEGFR2 inhibition both resulted in neutralization of the proliferative SW effect. (scale bar=100 μm) (*P<0.05 vs CTR). All experiments were performed at least in triplicate. C, VEGFR2 inhibition neutralizes anti‐apoptotic SW effect. HUVECs were starved, treated with VEGF antibody or VEGFR2 inhibitor, treated with SWT, and subsequently analyzed for apoptosis by TUNEL assay. SWT enhanced endothelial cell survival; however, effects were abolished with VEGF antibody or vandetanib pretreatment. (scale bar=100 μm) (*P<0.05 vs CTR). All experiments were performed at least in triplicate. D, Capillary sprouting after SWT is VEGFR2 dependent. Murine aortas were pretreated with VEGF antibody or VEGFR2 inhibitor and subsequently received SWT. Capillary sprouting after SWT was inhibited by VEGF antibody or VEGFR2 inhibitor pretreatment. (n=6 per group, *P<0.05 vs CTR). Akt indicates proteinkinase b; CTR, control; DAPI, 4′,diamidino‐2‐phenylindole; ERK, extracellular‐signal regulated kinase; HPF, high‐power field; INH, inhibitor; HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cell; SWT, shock wave therapy; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick‐end labeling; VEGFR2, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2.
