Figure 5.
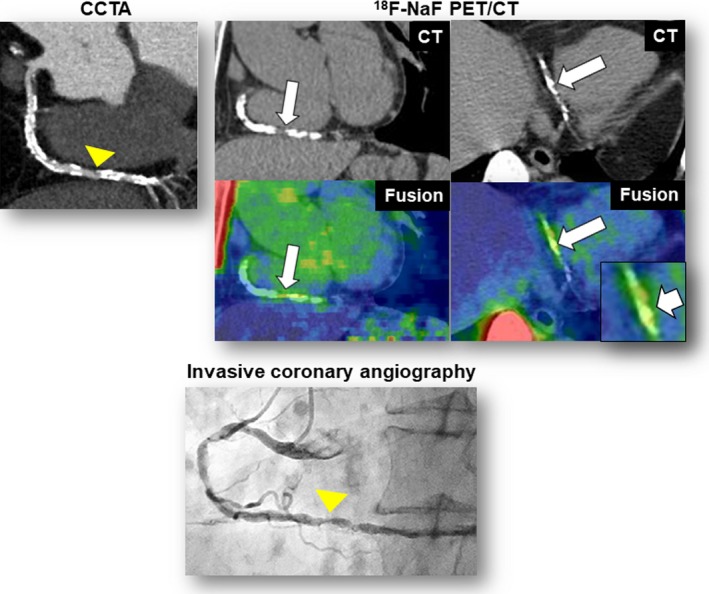
Additional representative case 1. CCTA revealed heavy coronary calcification and obstructive stenosis (≥70%) in the distal portion of the right coronary artery (CCTA, arrowhead). The fused PET/CT images showed enhanced 18F‐sodium fluoride (18F‐NaF) uptake corresponding to the calcification (maximum tissue‐to‐background ratio=1.6) (18F‐NaF PET/CT, arrows). This patient experienced unstable angina resulting from subtotal occlusion in the lesion corresponding to the calcification (invasive coronary angiography, arrow) 1 month after 18F‐NaF PET/CT scan. CCTA indicates coronary computed tomography angiography; CT, computed tomography; PET, positron emission tomography.
