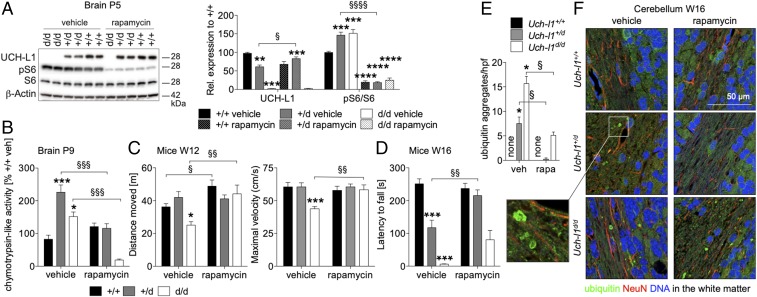
Fig. 8.
Postnatal rapamycin treatment ameliorates neurodegenerative phenotype of UCH-L1–deficient mice. Litters from Uch-l1+/d females crossed with Uch-l1+/d males were treated on a daily basis with rapamycin (0.1 mg/kg) or vehicle (NaCl/ethanol) from postnatal day 1–8. Thereafter, treatment was stopped. (A) WB for the phosphorylation (p) status of mTORC1 substrate S6 ribosomal protein (S6) in brains from one litter. Graph demonstrates densitometric quantification; 4 litters n = 6–22; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 to Uch-l1+/+; §P < 0.05, §§§§P < 0.0001 to Uch-l1+/d vehicle. (B) Chymotrypsin-like activity of the proteasome in brain lysates postnatal day 9 (P9), 24 h after termination of short-term treatment with rapamycin or vehicle; 3 litters n = 3–11; *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 to Uch-l1+/+ vehicle; §§§P < 0.001 genotype comparison. (C) Measurement of the distance moved in the open field test and the maximal velocity performed at 12 wk of age, demonstrating partially rescued phenotype in Uch-l1d/d mice; 5 litters n = 5–17; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 to Uch-l1+/+ vehicle; §P < 0.05; §§P < 0.01 genotype comparison. (D) Accelerated rotarod tests performed at 16 wk of age, demonstrating rescued neurological phenotype in Uch-l1+/d mice, 5 litters n = 2–15; ***P < 0.001 to Uch-l1+/+ vehicle, §§P < 0.01 to Uch-l1+/d vehicle. (E and F) Ubiquitin aggregates within the cerebellar white matter were quantified (E) and visualized (F) by immunofluorescent staining for ubiquitin (green), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP, red), and DNA (blue). Graph exhibits quantification of five high power fields (hpf) of n = 3 mice per genotype and treatment; *P < 0.05 to vehicle Uch-l1+/+; §P < 0.05 to respective vehicle-treated genotype.